什么是change stream?为什么需要它?
change stream是MongoDB提供的CDC解决方案。
Change streams allow applications to access real-time data changes without the complexity and risk of tailing the oplog.
tailing oplog在CDC (change data capture)场景下使用起来非常不便。
- oplog理论上仅供内部replication使用:
- 比如noop oplog、migrate 对用户来说没有意义
- 比如5.0引入了diff格式,oplog格式发生了变化,而且没有文档说明
- 比如事务相关的oplog有一系列的解析规则
- ……
- 分片集群下每个shard都有自己的oplog,排序和断点续传复杂
- 如果只需要关注某个表的数据变更,也要把oplog全部读出来,然后在客户端过滤
- 扩展性差,oplog只是普通的数据,定制化逻辑需要客户端实现,比如post-image、pre-image等等
Applications can use change streams to subscribe to all data changes on a single collection, a database, or an entire deployment, and immediately react to them.
change stream支持库表级别的监听,相比tailing oplog,易用性更强、而且节省了网络传输和客户端的资源消耗。
Because change streams use the aggregation framework, applications can also filter for specific changes or transform the notifications at will.
有着aggregate框架的加成,change stream扩展性更强。比如支持获取PreImages和PostImages,也支持UpdateLookUp。
change stream的缺点:
- 早期内核版本实现不完善。自3.6版本引入,后续版本对DDL操作支持不够,到6.0版本有所改善
- 资源开销较大,性能跟不上
总体流程
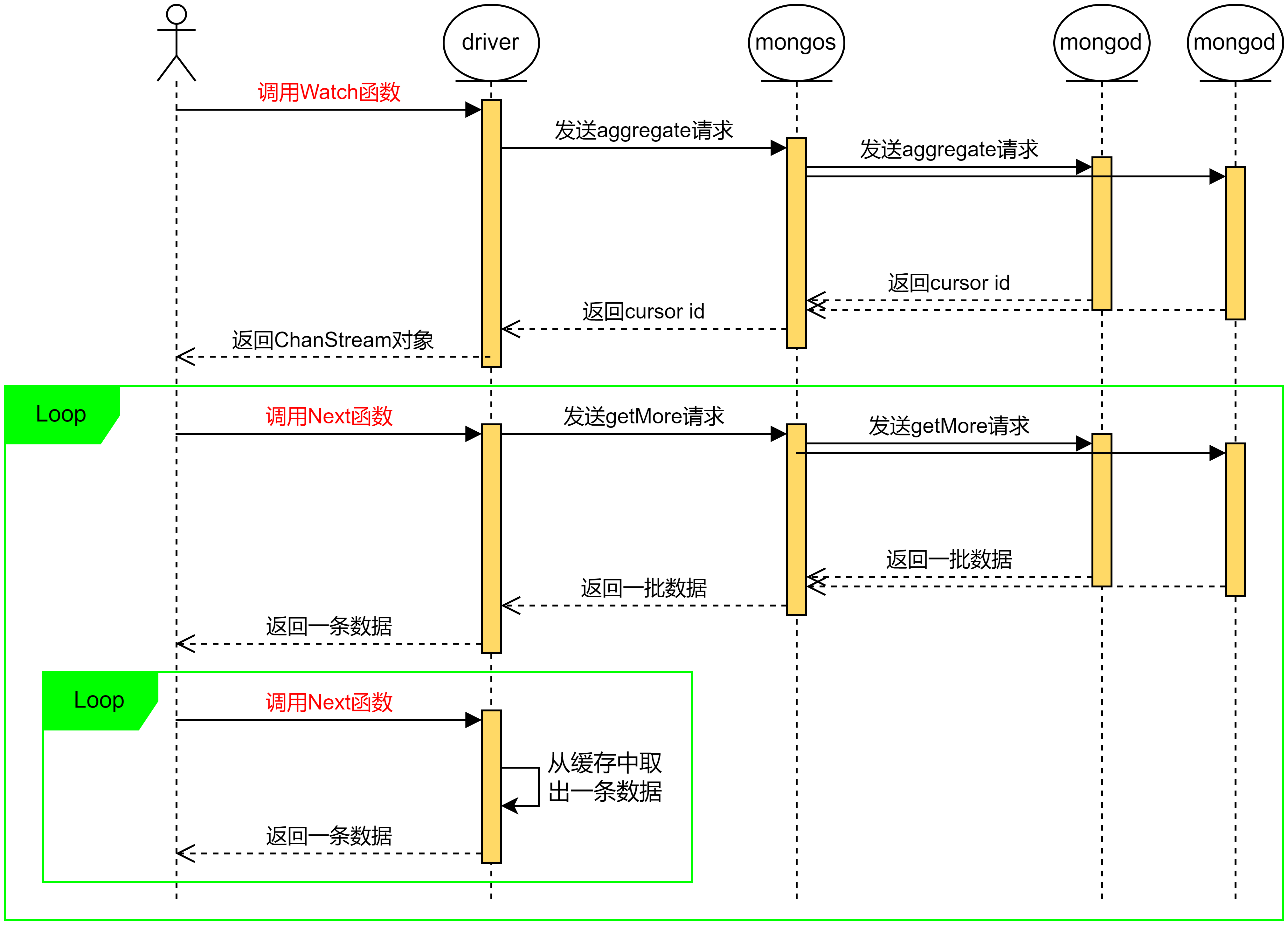
- 客户端调用driver的watch函数
- driver向mongos发送aggregate请求
- mongos向各个shard 发送aggregate请求
- 各个shard把各自的cursor返回给mongos
- mongos返回一个cursor给driver
- driver返回对象给客户端
- 客户端后续调用driver的next函数
- driver发送getMore给mongos,请求更多数据
- mongos向各个shard发送getMore请求
- 各个shard返回数据给mongos
- mongos返回数据给driver
- driver返回数据给客户端
客户端程序如下所示:
func run(cli *mongo.Client, ts primitive.Timestamp) error {
cs, err := clie.Watch(context.Background(), bson.A{}, &options.ChangeStreamOptions{
StartAtOperationTime: &ts,
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
for cs.Next(context.Background()) {
var doc bson.D
err = bson.Unmarshal(cs.Current, &doc)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// other code to consume doc
}
return cs.Err()
}
后面主要分享mongodb内核对change stream相关的处理,也上面的步骤2~11。基于https://github.com/mongodb/mongo/tree/v4.2 代码分析。
带着问题看下面的讲解:
- 如何汇聚、排序多个shard上的事件?
- 如何做断点续传?不同于tailing oplog,要考虑到长时间没有事件的情况。
- 如何处理事务相关的事件?
- 性能差在哪?
详细流程
下面以一个真实的change stream使用场景为例,遵循时间顺序依次讲解mongos和mongod的处理逻辑。
mongos处理driver发来的aggregate请求
请求:
{
aggregate: 1,
pipeline: [
{
'$changeStream': {
allChangesForCluster: true,
startAtOperationTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997099, i: 0 }),
}
}
],
cursor: {},
lsid: { id: new UUID("14265384-a9d8-4aa5-a60c-f95d499ea833") },
'$clusterTime': {
clusterTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997490, i: 1 }),
signature: {
hash: Binary("000000000000000000000000000000"),
keyId: Long("0")
}
},
'$db': 'admin'
}
mongos返回一个cursor id给driver:
{
cursor: {
firstBatch: {},
postBatchResumeToken: {_data: "8200000001000000002B0229296E04"},
id: 9208559579072114181,
ns: admin.$cmd.aggregate
},
ok: 1,
operationTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 }),
$clusterTime: {
clusterTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698998143, i: 1 }),
signature: {
hash: Binary("00000000000000000000000"),
keyId: Long("0")
}
}
}
下面来探究mongos是如何处理这个请求的:
代码处理流程:
ClusterPipelineCommand::run src/mongo/s/commands/cluster_pipeline_cmd.cpp
ClusterAggregate::runAggregate src/mongo/s/query/cluster_aggregate.cpp
LiteParsedPipeline::LiteParsedPipeline
LiteParsedDocumentSource::parse
DocumentSourceChangeStream::LiteParsed::parse
ClusterAggregate::runAggregate
Pipeline::parse // 构建pipeline
Pipeline::parseTopLevelOrFacetPipeline
DocumentSource::parse
DocumentSourceChangeStream::createFromBson
buildPipeline
sharded_agg_helpers::dispatchShardPipeline
mustRunOnAllShards
cluster_aggregation_planner::splitPipeline // 分离pipeline
findSplitPoint
createCommandForTargetedShards
genericTransformForShards
establishShardCursors // 在每个shard上创建cursor
establishCursors
dispatchMergingPipeline // 创建在mongos运行的pipeline
cluster_aggregation_planner::addMergeCursorsSource
DocumentSourceMergeCursors::create
runPipelineOnMongoS // 在mongos上运行pipeline
establishMergingMongosCursor // 建立一个总的cursor
cluster_aggregation_planner::buildClusterCursor
ccc->next(kInitialFind)
RouterStagePipeline::next
Pipeline::getNext // return EOF
DocumentSourceCloseCursor::getNext
DocumentSourceUpdateOnAddShard::getNext
DocumentSourceMergeCursors::getNext
setPostBatchResumeToken(ccc->getPostBatchResumeToken())
RouterStagePipeline::getPostBatchResumeToken
DocumentSourceMergeCursors::getHighWaterMark
BlockingResultsMerger::getHighWaterMark
AsyncResultsMerger::getHighWaterMark
registerCursor // 保存cursor信息,等待getMore请求
最初构建的pipeline,是由如下几个stage组成:
- DocumentSourceOplogMatch (不要与DocumentSourceMatch混淆)
- DocumentSourceChangeStreamTransform
- DocumentSourceCheckInvalidate
- DocumentSourceCheckResumability
- DocumentSourceCloseCursor
前4个stage是shard stage,不会运行在mongos上。对于mongos来说这四个stage的意义就是生成发送给shard的命令,之后会把这几个stage丢弃。DocumentSourceCloseCursor是merge stage,要在mongos上做,merge的时候以_id._data 的值排序。
cluster_aggregation_planner::addMergeCursorsSource 函数中,真正建立了要在mongos运行的pipeline(数据从上往下流动):
- DocumentSourceMergeCursors
- DocumentSourceUpdateOnAddShard
- DocumentSourceCloseCursor
建立好pipeline之后,会调用getNext运行一下,初始化各个stage,从各个shard拿到cursor id和post batch resume token,之后返回EOF。
mongod处理mongos发来的aggregate请求
mongos向mongod发送的aggregate请求如下:(pipeline跟driver发送给mongos的pipeline一样) 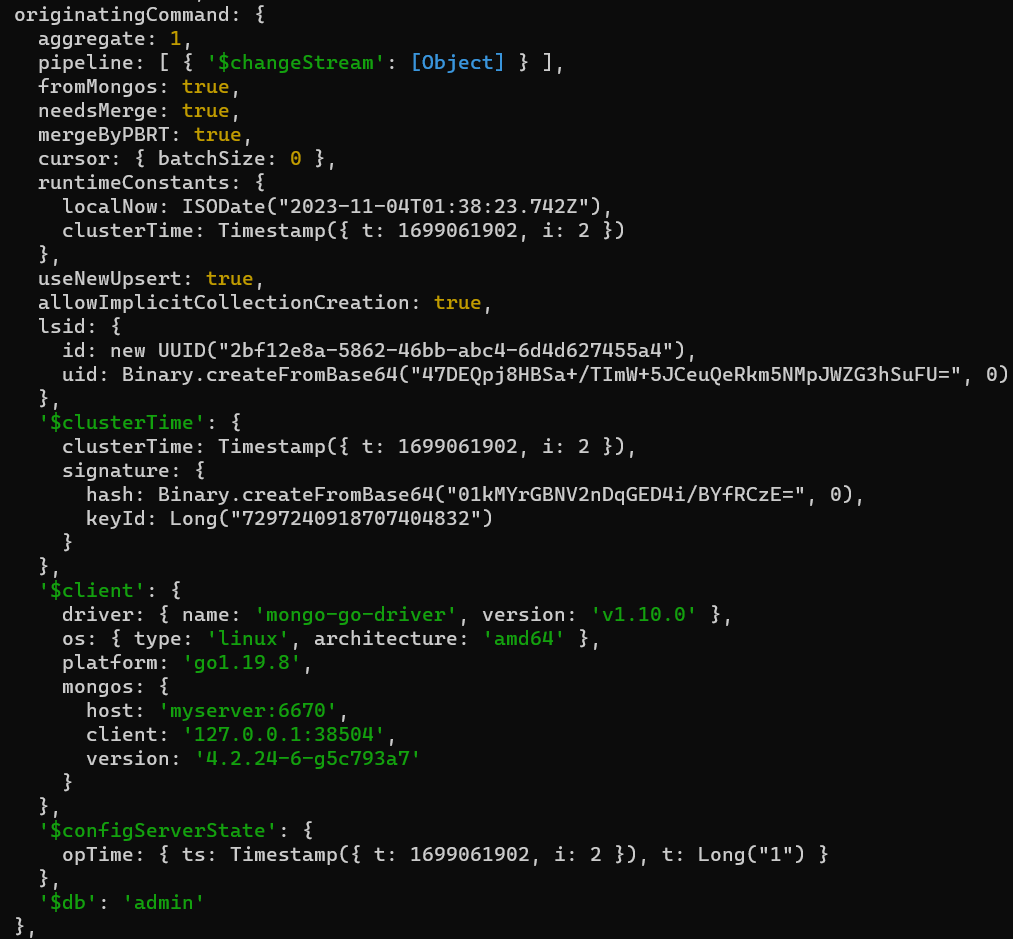
mongod把cursor id返回给mongos:
{
cursor: {
firstBatch: {},
postBatchResumeToken: {_data: "8200000001000000002B0229296E04"},
id: 9208559579072114181,
ns: admin.$cmd.aggregate
},
$_internalLatestOplogTimestamp: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 }),
ok: 1,
operationTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 }),
$gleStats: {
lastOpTime: Timestamp({ t: 1234356, i: 0 }),
electionId: ObjectID("7fffffff0000000000000001")
},
lastCommittedOpTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 }),
$configServerState: {
opTime: { ts: Timestamp({ t: 1698998143, i: 1 }), t: Long("1") }
},
$clusterTime: {
clusterTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698998143, i: 1 }),
signature: {
hash: Binary("00000000000000000000000"),
keyId: Long("0")
}
}
operationTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 }),
}
代码处理流程
PipelineCommand::Invocation::run
runAggregate src/mongo/db/commands/run_aggregate.cpp
LiteParsedPipeline::LiteParsedPipeline
LiteParsedDocumentSource::parse
DocumentSourceChangeStream::LiteParsed::parse
Pipeline::parse // 构建pipeline,mongos走的也是这个
Pipeline::parseTopLevelOrFacetPipeline
DocumentSource::parse
DocumentSourceChangeStream::createFromBson
buildPipeline
DocumentSourceChangeStream::buildMatchFilter
PipelineD::buildInnerQueryExecutor // 创建aggregate框架下层的executor
PipelineD::buildInnerQueryExecutorGeneric
PipelineD::prepareExecutor // 生成对local.oplog.rs的执行计划
attemptToGetExecutor
getExecutorFind
_getExecutorFind
getOplogStartHack
WiredTigerRecordStore::oplogStartHack // 给出collection scan的起始位置
PipelineD::attachInnerQueryExecutorToPipeline
DocumentSourceCursor::create
PipelineD::addCursorSource
Pipeline::addInitialSource
createOuterPipelineProxyExecutor // 为change stream加一个proxy stage
ChangeStreamProxyStage::ChangeStreamProxyStage
PipelineProxyStage::PipelineProxyStage
registerCursor // 保存cursor
handleCursorCommand
setPostBatchResumeToken(exec->getPostBatchResumeToken())
PlanExecutorImpl::getPostBatchResumeToken
ChangeStreamProxyStage::getPostBatchResumeToken
跟mongos差不多,最初构建的pipeline由如下几个stage组成:
- DocumentSourceOplogMatch (不要与DocumentSourceMatch类混淆)
- DocumentSourceChangeStreamTransform
- DocumentSourceCheckInvalidate
- DocumentSourceCheckResumability
最后经过调整,pipeline是这样:
- CollectionScan
- DocumentSourceCursor
- DocumentSourceChangeStreamTransform
- DocumentSourceCheckInvalidate
- DocumentSourceCheckResumability
- ChangeStreamProxyStage
mongos收到driver发来的getMore请求
请求如下:
{
getMore: Long("6439458890814903597"),
collection: '$cmd.aggregate',
lsid: { id: new UUID("14265384-a9d8-4aa5-a60c-f95d499ea833") },
'$clusterTime': {
clusterTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 }),
signature: {
hash: Binary("000000000000000000000000000000000"),
keyId: Long("0")
}
},
'$db': 'admin'
}
mongos返回数据给driver:
{
cursor: {
id: 9208559579072114181,
ns: admin.$cmd.aggregate,
nextBatch: {},
postBatchResumeToken: {_data: "8200000001000000002B0229296E04"}
},
ok: 1,
operationTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 }),
$clusterTime: {
clusterTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698998143, i: 1 }),
signature: {
hash: Binary("00000000000000000000000"),
keyId: Long("0")
}
}
}
代码处理流程
ClusterGetMoreCmd::Invocation::run
ClusterFind::runGetMore
cursorManager->checkOutCursor
ClusterCursorManager::PinnedCursor::next
ClusterClientCursorImpl::next
RouterStagePipeline::next
Pipeline::getNext
DocumentSourceCloseCursor::getNext
DocumentSourceUpdateOnAddShard::getNext
DocumentSourceMergeCursors::getNext
BlockingResultsMerger::next
BlockingResultsMerger::awaitNextWithTimeout
BlockingResultsMerger::getNextEvent
AsyncResultsMerger::nextEvent
AsyncResultsMerger::_scheduleGetMores
mongos对driver发送来的getMore请求处理比较简单:
- 取出cursor
- 调用next
- 底层stage发送getMore请求给mongod,获取数据
下面先看mongod如何处理getMore请求,以及返回给mongos什么数据。然后再看mongos如何返回数据给客户端。
mongod处理mongos发来的getMore请求
请求如下: 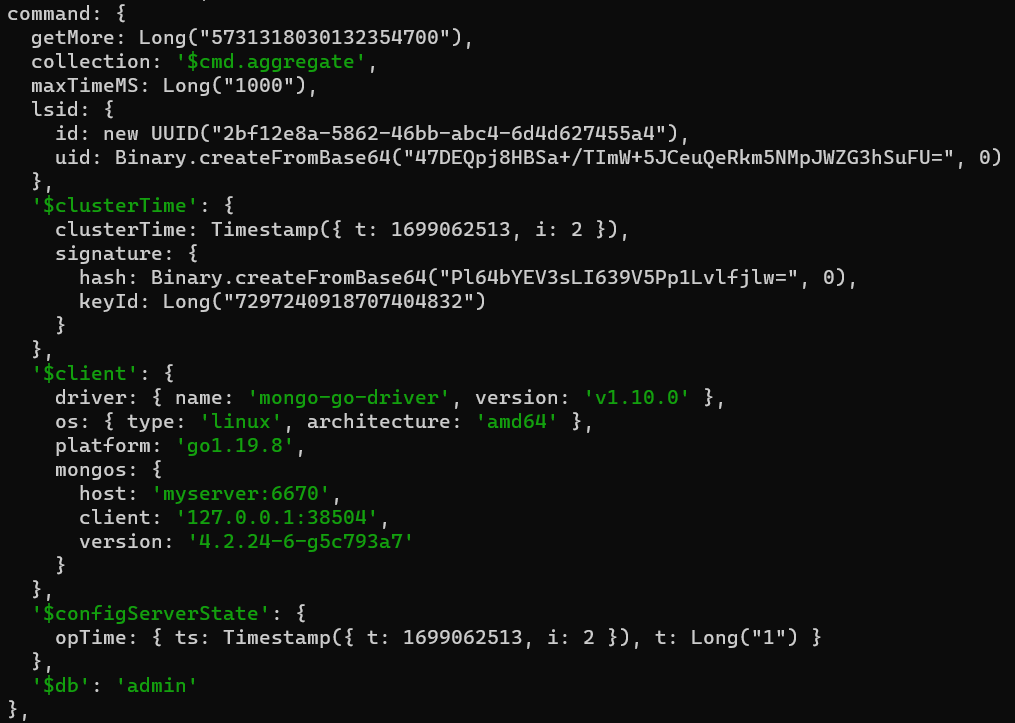
之后,mongod把数据返回给mongos:
{
cursor: {
nextBatch: {},
postBatchResumeToken: {_data: "8200000001000000002B0229296E04"},
id: 9208559579072114181,
ns: admin.$cmd.aggregate
},
$_internalLatestOplogTimestamp: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 }),
ok: 1,
$gleStats: {
lastOpTime: Timestamp({ t: 0, i: 0 }),
electionId: ObjectID("7fffffff0000000000000001")
},
lastCommittedOpTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 }),
$configServerState: {
opTime: { ts: Timestamp({ t: 1698998143, i: 1 }), t: Long("1") }
},
$clusterTime: {
clusterTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698998143, i: 1 }),
signature: {
hash: Binary("00000000000000000000000"),
keyId: Long("0")
}
},
operationTime: Timestamp({ t: 1698997500, i: 1 })
}
这里面有两个重要的东西nextBatch和postBatchResumeToken,分别是数据和断点续传标记。下面重点看这两个东西怎么来的。
代码处理流程
GetMoreCmd::Invocation::run
GetMoreCmd::Invocation::acquireLocksAndIterateCursor
GetMoreCmd::Invocation::generateBatch
PlanExecutorImpl::getNext
PlanExecutorImpl::_getNextImpl
PlanStage::work
PipelineProxyStage::doWork (ChangeStreamProxyStage继承自PipelineProxyStage)
ChangeStreamProxyStage::getNextBson
Pipeline::getNext
DocumentSourceCheckResumability::getNext
DocumentSourceCheckInvalidate::getNext
DocumentSourceChangeStreamTransform::getNext
DocumentSourceCursor::getNext
DocumentSourceCursor::loadBatch
...
CollectionScan::doWork
setPostBatchResumeToken(exec->getPostBatchResumeToken())
PlanExecutorImpl::getPostBatchResumeToken
ChangeStreamProxyStage::getPostBatchResumeToken // read _postBatchResumeToken
跟mongos一样,取出cursor之后,就开始走pipeline流程。下面从数据流动的方向开始讲解:
CollectionScan
query长这样: 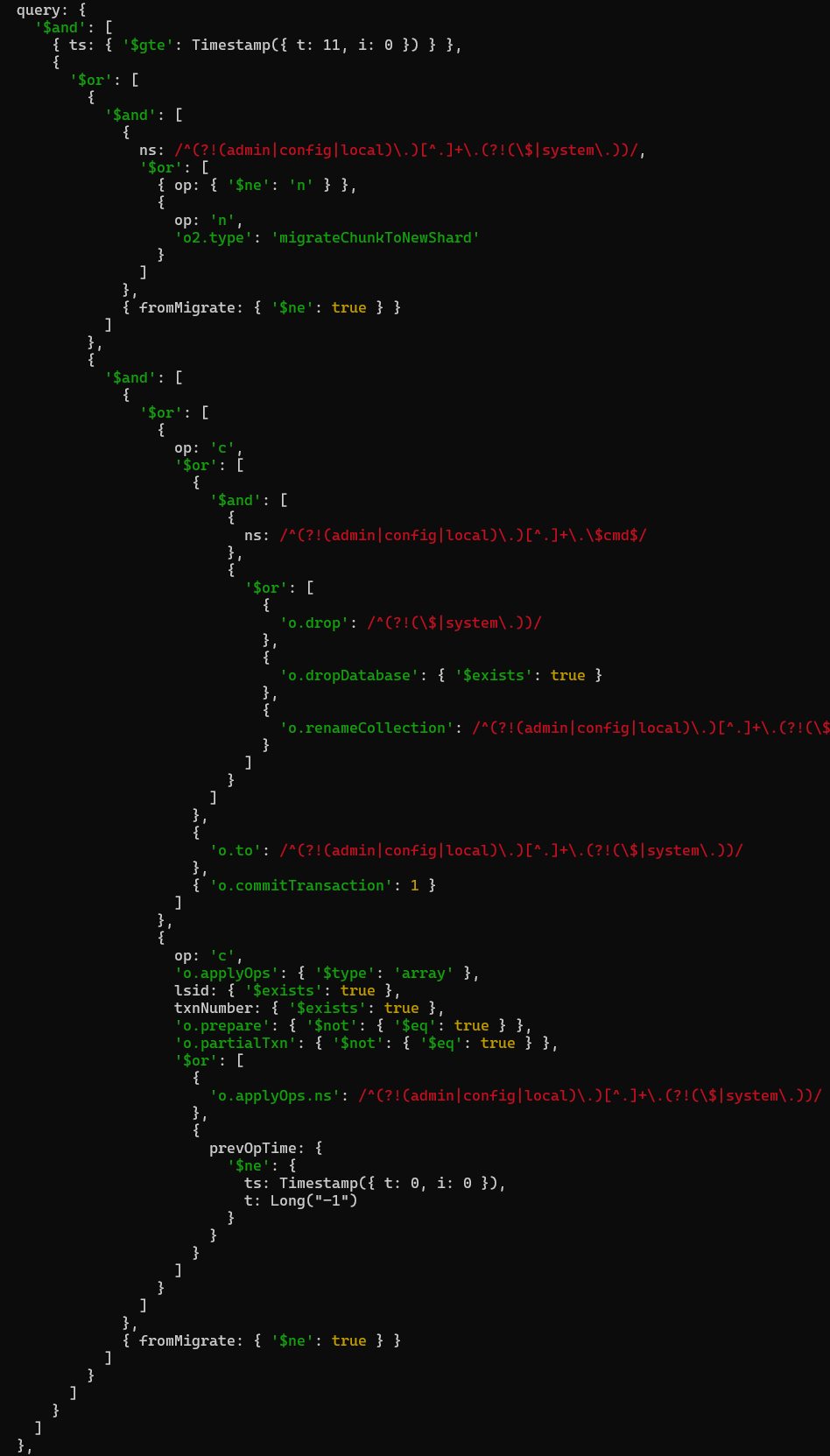
过滤条件有很多:
- oplog 的ts大于等于 {11,0} 。这个时间戳是客户端指定的,通过mongos透传到各个shard,用作断点续传。
- 考虑一个问题:不同的shard有不同的时间,仅用一个时间戳用作断点续传有没有问题?
- 捕获fromMigrate为false,非admin、config、local库且op不是n的oplog
- 捕获fromMigrate为false,op是n,且o2.type为migrateChunkToNewShard的oplog
- 另外捕获了drop、dropDatabase、renameCollection、commitTransaction、applyOps等DDL操作
collectionScan不是从头开始的,而是从小于等于客户端指定时间戳,且最近的那条oplog开始。如果所有oplog的ts都比客户端指定时间戳大,collectionScan就从头开始。然后collectionScan会检查这条oplog,如果不满足下面任一条件,就说明oplog被冲了,会抛出ErrorCodes::OplogQueryMinTsMissing 异常。
- 此oplog是类型是n,o.msg是initiating set。表示这是一个新副本集。具体见CollectionScan::assertMinTsHasNotFallenOffOplog 函数
- 此oplog的ts小于等于给定的ts
只要有一个shard上的oplog被冲了,change stream命令就会报错。
可以修改了这个filter,来捕获更多的oplog。
另外需要关注,CollectionScan每次返回文档之前都更新一下_latestOplogEntryTimestamp:
Status CollectionScan::setLatestOplogEntryTimestamp(const Record& record) {
auto tsElem = record.data.toBson()[repl::OpTime::kTimestampFieldName];
_latestOplogEntryTimestamp = std::max(_latestOplogEntryTimestamp, tsElem.timestamp());
return Status::OK();
}
DocumentSourceCursor
DocumentSourceCursor对接CollectionScan等普通查询,作为aggregate pipeline的数据来源。
这里注意一下_latestOplogTimestamp这个私有变量,每次getNext都会被更新:
DocumentSource::GetNextResult DocumentSourceCursor::getNext() {
// ......
// If we are tracking the oplog timestamp, update our cached latest optime.
if (_trackOplogTS && _exec)
_updateOplogTimestamp();
// ......
}
void DocumentSourceCursor::_updateOplogTimestamp() {
// If we are about to return a result, set our oplog timestamp to the optime of that result.
if (!_currentBatch.isEmpty()) {
const auto& ts = _currentBatch.peekFront().getField(repl::OpTime::kTimestampFieldName);
invariant(ts.getType() == BSONType::bsonTimestamp);
_latestOplogTimestamp = ts.getTimestamp(); // 设置为要返回的oplog的ts
return;
}
// If we have no more results to return, advance to the latest oplog timestamp.
_latestOplogTimestamp = _exec->getLatestOplogTimestamp(); // 从collection scan取时间戳
}
Timestamp CollectionScan::getLatestOplogTimestamp() const {
return _latestOplogEntryTimestamp;
}
DocumentSourceChangeStreamTransform
这个stage负责把oplog转换成event。
DocumentSource::GetNextResult DocumentSourceChangeStreamTransform::getNext() {
while (1) {
// If we're unwinding an 'applyOps' from a transaction, check if there are any documents we
// have stored that can be returned.
if (_txnIterator) {
if (auto next = _txnIterator->getNextTransactionOp(pExpCtx->opCtx)) {
return applyTransformation(*next);
}
_txnIterator = boost::none;
}
// Get the next input document.
auto input = pSource->getNext();
if (!input.isAdvanced()) {
return input;
}
auto doc = input.releaseDocument();
auto op = doc[repl::OplogEntry::kOpTypeFieldName];
auto opType =
repl::OpType_parse(IDLParserErrorContext("ChangeStreamEntry.op"), op.getStringData());
auto commandVal = doc["o"];
if (opType != repl::OpTypeEnum::kCommand ||
(commandVal["applyOps"].missing() && commandVal["commitTransaction"].missing())) {
return applyTransformation(doc);
}
// The only two commands we will see here are an applyOps or a commit, which both mean we
// need to open a "transaction context" representing a group of updates that all occurred at
// once as part of a transaction.
invariant(!_txnIterator);
_txnIterator.emplace(pExpCtx->opCtx, pExpCtx->mongoProcessInterface, doc, *_nsRegex);
}
}
会把applyOps拆开处理。对于普通oplog,直接进行transform:
Document DocumentSourceChangeStreamTransform::applyTransformation(const Document& input) {
MutableDocument doc;
// Extract the fields we need.
string op = input[repl::OplogEntry::kOpTypeFieldName].getString();
Value ts = input[repl::OplogEntry::kTimestampFieldName];
Value ns = input[repl::OplogEntry::kNssFieldName];
Value uuid = input[repl::OplogEntry::kUuidFieldName];
std::vector<FieldPath> documentKeyFields;
// Deal with CRUD operations and commands.
auto opType = repl::OpType_parse(IDLParserErrorContext("ChangeStreamEntry.op"), op);
NamespaceString nss(ns.getString());
// Ignore commands in the oplog when looking up the document key fields since a command implies
// that the change stream is about to be invalidated (e.g. collection drop).
if (!uuid.missing() && opType != repl::OpTypeEnum::kCommand) {
documentKeyFields = _documentKeyCache.find(uuid.getUuid())->second.documentKeyFields;
}
Value id = input.getNestedField("o._id");
// Non-replace updates have the _id in field "o2".
StringData operationType;
Value fullDocument;
Value updateDescription;
Value documentKey;
switch (opType) {
case repl::OpTypeEnum::kInsert: {
operationType = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kInsertOpType;
fullDocument = input[repl::OplogEntry::kObjectFieldName];
documentKey = Value(document_path_support::extractPathsFromDoc(
fullDocument.getDocument(), documentKeyFields));
break;
}
case repl::OpTypeEnum::kDelete: {
operationType = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kDeleteOpType;
documentKey = input[repl::OplogEntry::kObjectFieldName];
break;
}
case repl::OpTypeEnum::kUpdate: {
if (id.missing()) {
// non-replace style update
operationType = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kUpdateOpType;
// ......
} else {
// replace style update
operationType = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kReplaceOpType;
fullDocument = input[repl::OplogEntry::kObjectFieldName];
}
documentKey = input[repl::OplogEntry::kObject2FieldName];
break;
}
case repl::OpTypeEnum::kCommand: {
if (!input.getNestedField("o.drop").missing()) {
operationType = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kDropCollectionOpType;
nss = NamespaceString(nss.db(), input.getNestedField("o.drop").getString());
} else if (!input.getNestedField("o.renameCollection").missing()) {
operationType = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kRenameCollectionOpType;
// ......
} else if (!input.getNestedField("o.dropDatabase").missing()) {
operationType = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kDropDatabaseOpType;
nss = NamespaceString(nss.db());
} else {
// All other commands will invalidate the stream.
operationType = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kInvalidateOpType;
}
// Make sure the result doesn't have a document key.
documentKey = Value();
break;
}
case repl::OpTypeEnum::kNoop: {
operationType = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kNewShardDetectedOpType;
// Generate a fake document Id for NewShardDetected operation so that we can resume
// after this operation.
documentKey = Value(Document);
break;
}
default: { MONGO_UNREACHABLE; }
}
// Note that 'documentKey' and/or 'uuid' might be missing, in which case they will not appear
// in the output.
auto resumeTokenData = getResumeToken(ts, uuid, documentKey);
auto resumeToken = ResumeToken(resumeTokenData).toDocument();
// Add some additional fields only relevant to transactions.
if (_txnIterator) {
doc.addField(DocumentSourceChangeStream::kTxnNumberField,
Value(static_cast<long long>(_txnIterator->txnNumber())));
doc.addField(DocumentSourceChangeStream::kLsidField, Value(_txnIterator->lsid()));
}
doc.addField(DocumentSourceChangeStream::kIdField, Value(resumeToken));
doc.addField(DocumentSourceChangeStream::kOperationTypeField, Value(operationType));
doc.addField(DocumentSourceChangeStream::kClusterTimeField, Value(resumeTokenData.clusterTime));
doc.setSortKeyMetaField(resumeToken.toBson());
// ......
doc.addField(DocumentSourceChangeStream::kDocumentKeyField, documentKey);
// ......
}
这里就是对CURD操作和一些DDL操作进行了转换。需要注意的是
- 相比oplog,event多了replace、invalidate和kNewShardDetected等很多类型。
- oplog的ts字段被用来生成resume token,被用来当作event的clusterTime字段的值
- resume token同时作为 event的_id 和 sortKey
可以修改了这里,支持对更多类型的oplog进行转换。
DocumentSourceCheckInvalidate
这个stage检查event,如果符合下面条件就生成一个 invalidate类型的event:
- 要监听的ns、db被drop或者rename
DocumentSourceCheckResumability
这个stage做断点续传的恢复工作。
DocumentSource::GetNextResult DocumentSourceCheckResumability::getNext() {
if (_resumeStatus == ResumeStatus::kSurpassedToken) {
return pSource->getNext();
}
while (_resumeStatus != ResumeStatus::kSurpassedToken) {
// The underlying oplog scan will throw OplogQueryMinTsMissing if the minTs in the change
// stream filter has fallen off the oplog. Catch this and throw a more explanatory error.
auto nextInput = [this]() {
try {
return pSource->getNext();
} catch (const ExceptionFor<ErrorCodes::OplogQueryMinTsMissing>&) {
uasserted(ErrorCodes::ChangeStreamHistoryLost,
"Resume of change stream was not possible, as the resume point may no "
"longer be in the oplog.");
}
}();
// If we hit EOF, return it immediately.
if (!nextInput.isAdvanced()) {
return nextInput;
}
// Determine whether the current event sorts before, equal to or after the resume token.
_resumeStatus =
compareAgainstClientResumeToken(pExpCtx, nextInput.getDocument(), _tokenFromClient);
switch (_resumeStatus) {
case ResumeStatus::kCheckNextDoc:
// If the result was kCheckNextDoc, we are resumable but must swallow this event.
continue;
case ResumeStatus::kSurpassedToken:
// In this case the resume token wasn't found; it may be on another shard. However,
// since the oplog scan did not throw, we know that we are resumable. Fall through
// into the following case and return the document.
case ResumeStatus::kFoundToken:
// We found the actual token! Return the doc so DSEnsureResumeTokenPresent sees it.
return nextInput;
}
}
MONGO_UNREACHABLE;
}
这个getNext函数的意思是:
- oplog被冲,不可能恢复时,抛出ErrorCodes::ChangeStreamHistoryLost异常。
- 如果可以恢复,
- 能找到这个token,就从这个token开始吐出事件;
- 找不到这个token,说明这个token很可能是其他shard生成的,就从大于这个token的地方开始吐出事件。
目标是不返回重复事件。
ChangeStreamProxyStage
boost::optional<BSONObj> ChangeStreamProxyStage::getNextBson() {
if (auto next = _pipeline->getNext()) {
auto nextBSON = _validateAndConvertToBSON(*next);
_latestOplogTimestamp = PipelineD::getLatestOplogTimestamp(_pipeline.get());
_postBatchResumeToken = next->getSortKeyMetaField();
_setSpeculativeReadTimestamp();
return nextBSON;
}
// We ran out of results to return.
auto highWaterMark = PipelineD::getLatestOplogTimestamp(_pipeline.get());
if (highWaterMark > _latestOplogTimestamp) {
auto token = ResumeToken::makeHighWaterMarkToken(highWaterMark);
_postBatchResumeToken = token.toDocument().toBson();
_latestOplogTimestamp = highWaterMark;
_setSpeculativeReadTimestamp();
}
return boost::none;
}
PipelineD::getLatestOplogTimestamp()返回的就是DocumentSourceCursor::_latestOplogTimestamp。
这个stage做的主要工作就是维护postBatchResumeToken变量。postBatchResumeToken就是用作断点续传的resume token。
- 返回每个文档之前,都把postBatchResumeToken更新成这个文档的resume token
- 没有文档要返回时,就把postBatchResumeToken设置成一个high-water-mark resume token,它的ts是collectionScan里面的latest oplog timestamp。
为什么要有high-water-mark resume token?
想象一个场景——客户端watch一个collection,但是这个collection一直没有写入,如果postBatchResumeToken一直不推进,那等客户端拿着很旧的resume token续传时,发现无法恢复。high-water-mark resume token的意义就是即使没有客户端关注的事件产生,也能推进同步点。
mongos汇聚数据返回给driver
每个shard上的事件是有序的,shard间的事件依赖混合逻辑时钟拥有偏序关系。mongos的任务就是汇聚各个shard上的事件并排序,提供一个全局顺序。
代码处理流程
ClusterGetMoreCmd::Invocation::run
ClusterFind::runGetMore
cursorManager->checkOutCursor
ClusterCursorManager::PinnedCursor::next
ClusterClientCursorImpl::next
RouterStagePipeline::next
Pipeline::getNext
DocumentSourceCloseCursor::getNext
DocumentSourceUpdateOnAddShard::getNext
DocumentSourceMergeCursors::getNext
DocumentSourceMergeCursors::getNext
DocumentSourceMergeCursors::getNext
BlockingResultsMerger::next
BlockingResultsMerger::awaitNextWithTimeout
BlockingResultsMerger::getNextEvent
AsyncResultsMerger::nextEvent (整个函数持有_mutex)
AsyncResultsMerger::_scheduleGetMores
AsyncResultsMerger::_askForNextBatch
TaskExecutor::scheduleRemoteCommand
AsyncResultsMerger::_handleBatchResponse
AsyncResultsMerger::_processBatchResults
AsyncResultsMerger::_addBatchToBuffer
AsyncResultsMerger::_updateRemoteMetadata
AsyncResultsMerger::nextReady
AsyncResultsMerger::_nextReadySorted
汇聚各个shard上的事件并做排序其实很简单,就是一个归并排序。
这里的核心是AsyncResultsMerger。给每个shard维护了一个docBuffer queue,用来存放getMore response里面的events。每次会按照_id._data对比所有docBuffer queue的第一条文档,返回最小的那条。 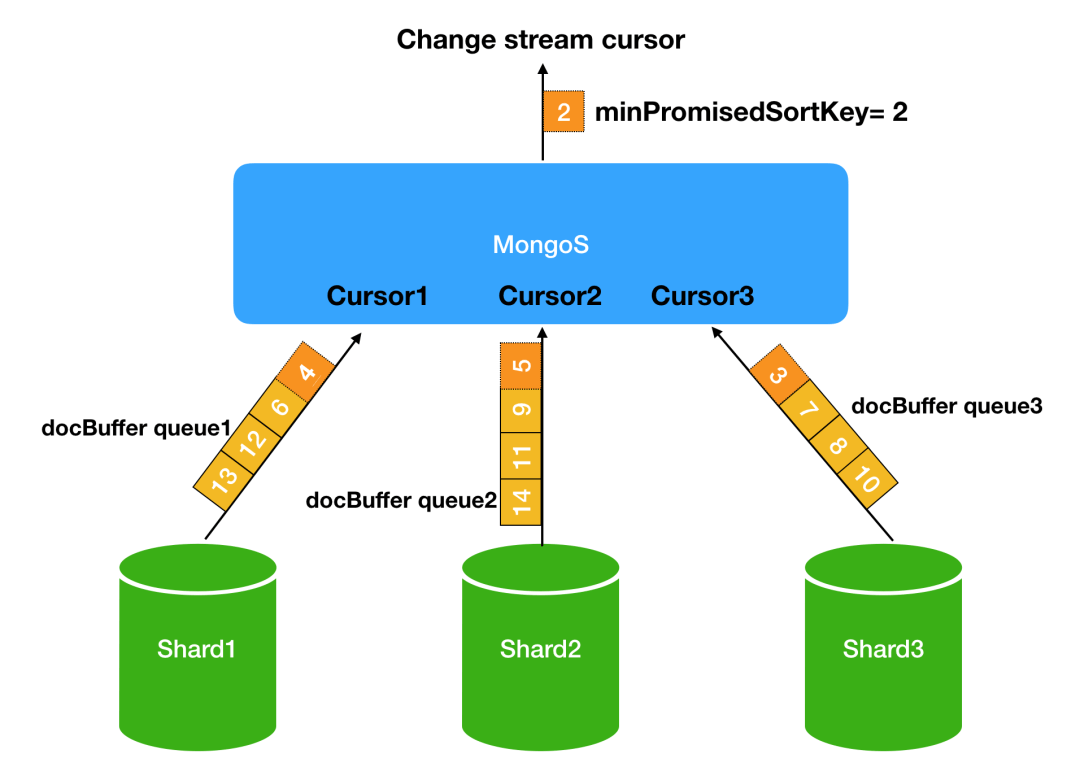
这里有个问题需要考虑:如果一个shard的docBuffer目前是空,mongos该怎么办呢?
- 一种可能是网络问题或者mongod负载高,响应慢了;
- 另一种可能是这个shard上根本就没有事件产生。
如果是因为响应慢了,必须要多等会,否则无法保证全局顺序;如果是因为没有事件,不需要等待。
那么,到底等不等呢?如何适配这两种情况?
这里就要讲到 Post Batch Resume Token(简称PBRT)和 minPromisedSortKey的概念了。前面已经简单介绍过mongod是怎么产生PBRT的——PBRT要么是最近事件的resume token,要么是已扫描的最新oplog的时间戳构成的high-water-mark resume token,取决于是否遇到EOF。PBRT也可以看作是shard给mongos的一个承诺——承诺后面返回的事件都大于等于这个时间戳。mongos从所有shard的PBRT中取一个最小值,叫做minPromisedSortKey。有了minPromisedSortKey就可以解决上面的问题了。
解决方法就是mongos每次返回事件之前都跟minPromisedSortKey对比,
- 如果小于等于minPromisedSortKey,说明可以安全返回。
- 如果大于minPromisedSortKey,说明有些shard“响应慢了“,需要等待。
总的来说,mongos的处理策略如下:
- 在向所有shard发出aggregate请求之后,每个shard都会把自己的cursor id和PBRT返回给mongos。mongos会等待所有shard响应之后,根据所有的PBRT得到minPromisedSortKey。在此之前不向客户端返回数据。
- 在客户端不断getMore过程中,如果当前最小的event(对比所有非空docBuffer的第一个event)比minPromisedSortKey要大,就不返回数据,等待minPromisedSortKey的推进。
- 每次收到来自shard的PBRT,都会更新minPromisedSortKey。
bool AsyncResultsMerger::_readySortedTailable(WithLock lk) {
if (_mergeQueue.empty()) {
return false;
}
auto smallestRemote = _mergeQueue.top();
auto smallestResult = _remotes[smallestRemote].docBuffer.front();
auto keyWeWantToReturn =
extractSortKey(*smallestResult.getResult(), _params.getCompareWholeSortKey());
// We should always have a minPromisedSortKey from every shard in the sorted tailable case.
auto minPromisedSortKey = _getMinPromisedSortKey(lk);
invariant(!minPromisedSortKey.isEmpty());
return compareSortKeys(keyWeWantToReturn, minPromisedSortKey, *_params.getSort()) <= 0;
}
这样mongos就可以向客户端吐出全局有序的数据流了。mongos发送给客户端的每个响应中都带有一批events和postBatchResumeToken字段,postBatchResumeToken就是resume token,用作断点续传。这个字段的值
- 在不等待的时候,是已返回的最新event的sort key的值
- 在等待的时候,是minPromisedSortKey 。这样即使没有事件产生,客户端也能知道最新的resume token。
DocumentSourceUpdateOnAddShard::getNext
DocumentSource::GetNextResult DocumentSourceUpdateOnAddShard::getNext() {
auto childResult = pSource->getNext();
while (childResult.isAdvanced() && needsUpdate(childResult.getDocument())) {
addNewShardCursors(childResult.getDocument());
childResult = pSource->getNext();
}
return childResult;
}
// Returns true if the change stream document has an 'operationType' of 'newShardDetected'.
bool needsUpdate(const Document& childResult) {
return childResult[DocumentSourceChangeStream::kOperationTypeField].getStringData() ==
DocumentSourceChangeStream::kNewShardDetectedOpType;
}
当有chunk mirgrate到新的shard上,会产生kNewShardDetectedOpType event。这个stage遇到这个类型的event,就会建立通往新shard的cursor。
DocumentSourceCloseCursor::getNext
DocumentSource::GetNextResult DocumentSourceCloseCursor::getNext() {
pExpCtx->checkForInterrupt();
// Close cursor if we have returned an invalidate entry.
if (_shouldCloseCursor) {
uasserted(ErrorCodes::CloseChangeStream, "Change stream has been invalidated");
}
auto nextInput = pSource->getNext();
if (!nextInput.isAdvanced())
return nextInput;
auto doc = nextInput.getDocument();
const auto& kOperationTypeField = DocumentSourceChangeStream::kOperationTypeField;
auto operationType = doc[kOperationTypeField].getString();
if (operationType == DocumentSourceChangeStream::kInvalidateOpType) {
_shouldCloseCursor = true;
}
return nextInput;
}
当文件的operationType字段值为invalidate时,下次调用getNext,会抛出异常,关闭cursor。
resume token
resume token用作events的排序和change stream的恢复。
struct ResumeTokenData {
enum FromInvalidate : bool {
kFromInvalidate = true,
kNotFromInvalidate = false,
};
enum TokenType : int {
kHighWaterMarkToken = 0, // Token refers to a point in time, not an event.
kEventToken = 128, // Token refers to an actual event in the stream.
};
Timestamp clusterTime; // 如果是kEventToken,就等于oplog的cluster time
int version = 1;
TokenType tokenType = TokenType::kEventToken;
size_t txnOpIndex = 0;
// Flag to indicate that this resume token is from an "invalidate" entry. This will not be set
// on a token from a command that *would* invalidate a change stream, but rather the invalidate
// notification itself.
FromInvalidate fromInvalidate = FromInvalidate::kNotFromInvalidate;
boost::optional<UUID> uuid;
Value documentKey; // _id + shard key
};
/* {
* _data: String, A hex encoding of the binary generated by keystring encoding the clusterTime,
* version, txnOpIndex, UUID, then documentKey in that order.
* _typeBits: BinData - The keystring typebuildMatchFilter bits used for deserialization.
* }
*/
class ResumeToken {
public:
constexpr static StringData kDataFieldName = "_data"_sd;
constexpr static StringData kTypeBitsFieldName = "_typeBits"_sd;
// 把ResumeTokenData转为hex string
explicit ResumeToken(const ResumeTokenData& resumeValue);
// 把hex string转为ResumeTokenData
ResumeTokenData getData() const;
private:
// This is the hex-encoded string encoding all the pieces of the resume token.
std::string _hexKeyString;
// Since we are using a KeyString encoding, we might lose some information about what the
// original types of the serialized values were. For example, the integer 2 and the double 2.0
// will generate the same KeyString. We keep the type bits around so we can deserialize without
// losing information.
Value _typeBits; // 不参与比较,这个字段常常被忽略
};
要想排序,就要尽可能精确地描述event,尽量让每个event都有一个唯一的值。能够做到全局有序,那么恢复也不是什么难事。
ResumeTokenData里面有这些字段:
- clusterTime,表示了集群中事件的偏序关系。不同的shard可能产生有相同ts的event。events的ts相同,说明他们的先后顺序不重要。
- documentKey,不同的documentKey在同一时间一定属于不同的shard。有些event是没有documentKey的,比如DDL操作。
- txnOpIndex是针对多文档事务添加的。applyOps oplog里面会包括多个子oplog。
- tokenType和fromInvalidate 是为断点续传设计的。
- uuid,collection的uuid,直接沿用oplog的ui。
- version用做断点续传时兼容性判断,比如集群升级
- 3.6是第一个版本,clusterTime + documentKey + uuid
- 4.0.0 ~ 4.0.6 是v0版本,clusterTime + applyOpsIndex + documentKey + uuid
- v1版本就是这篇文章讲的
- 6.0开始引入了v2版本,主要变化就是documentKey字段变成了eventIdentifier字段,对于CURD操作还是当作documentKey使用,对于非CURD操作,用来记录operationDescription。开始支持更多的DDL操作。
最后总结一下这些时间戳:
- oplog entry 的ts
- change event的cluster time
- collection scan的latest oplog timestamp
- shard上维护的PBRT
- mongos上的minPromisedSortKey
- resume token,用作客户端断点续传
change stream的问题
DDL支持不完善的问题:
Starting in MongoDB 6.0, change streams support change notifications for DDL events, like the createIndexes and dropIndexes events. To include expanded events in a change stream, create the change stream cursor using the showExpandedEvents option.
延迟问题:
Sharded clusters with one or more shards that have little or no activity for the collection , or are “cold”, can negatively affect the response time of the change stream as the mongos must still check with those cold shards to guarantee total ordering of changes. To minimize latency for cold shards, you can specify a lower periodicNoopIntervalSecs value.
孤儿文档问题:
For sharded collections, update operations with multi : true may cause any change streams opened against that collection to send notifications for orphaned documents. Starting in MongoDB 5.3, during range migration, change stream events are not generated for updates to orphaned documents.
性能问题:
If a sharded collection has high levels of activity, the mongos may not be able to keep up with the changes across all of the shards. Consider utilizing notification filters for these types of collections. For example, passing a $match pipeline configured to filter only insert operations.
change stream在mongos、mongod上都会有一个线程。当集群写入量比较大时,相关mongos、mongod上那个线程的cpu常常是100%。
副本集火焰图: 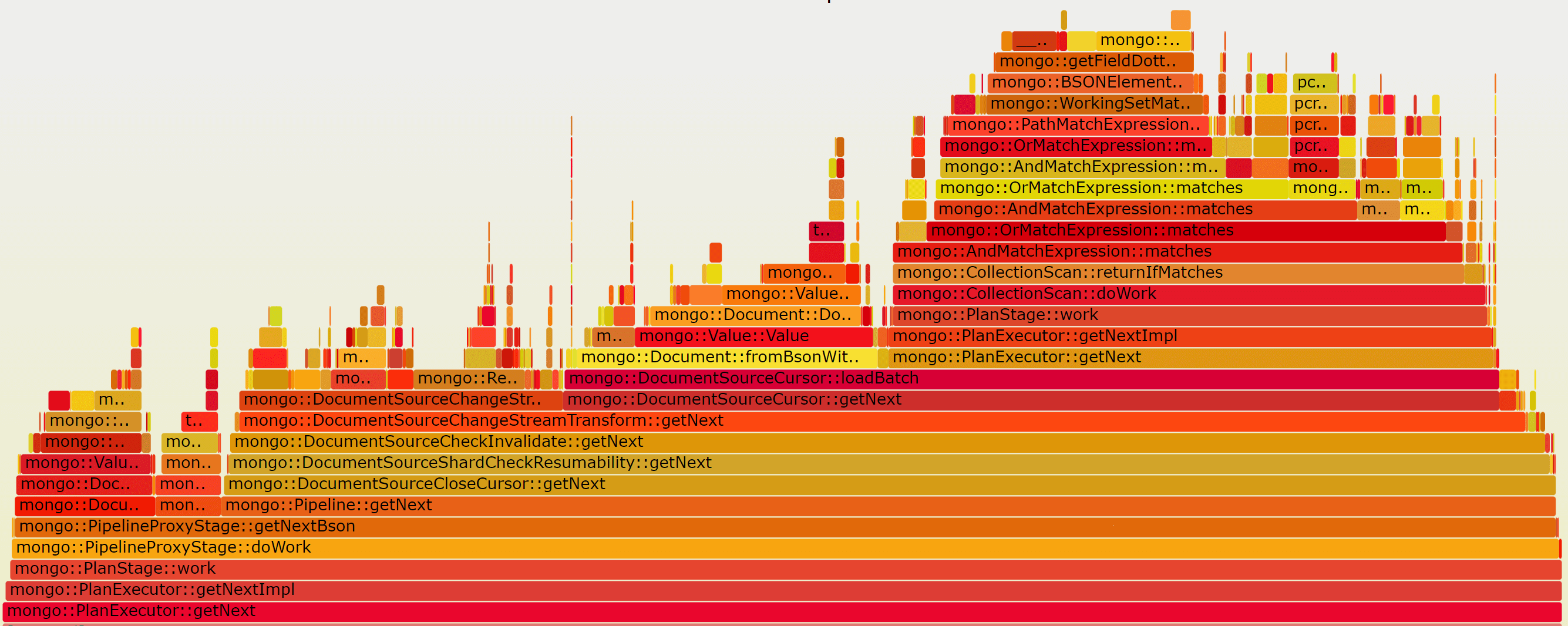
mongod cpu主要花在match和transform两个阶段。
分片集群mongos火焰图: 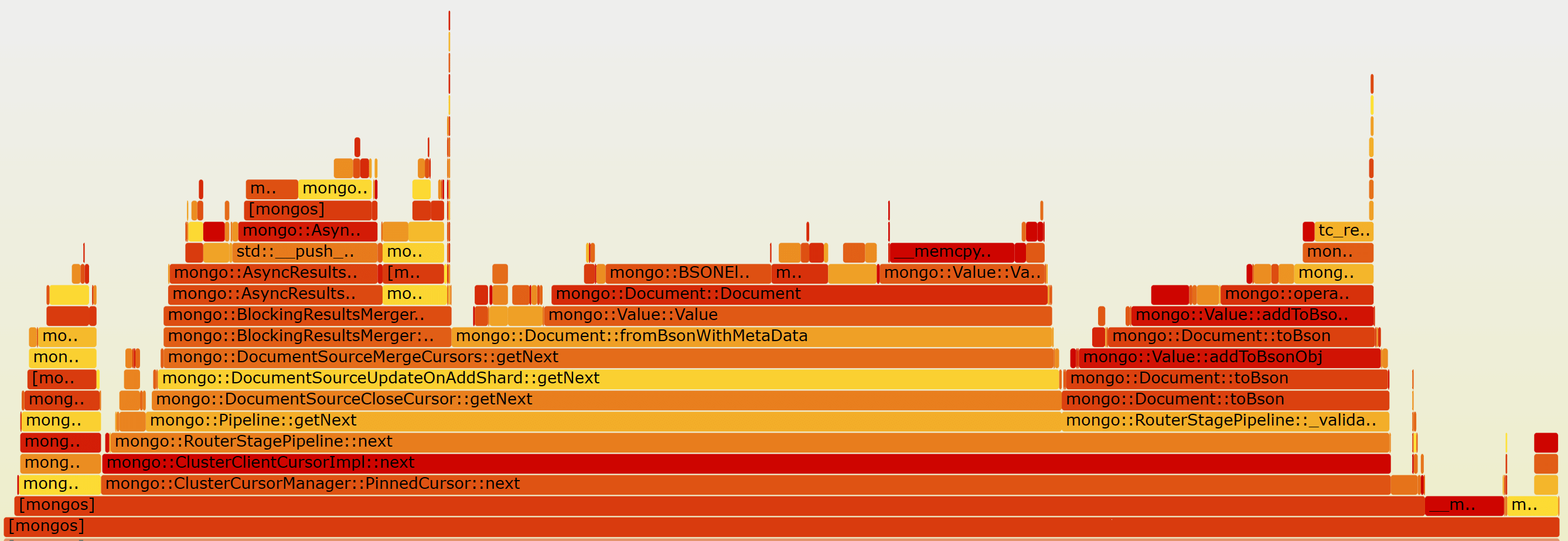 mongos的cpu主要花在排序——resume token的对比,和document与bson之间的转换。
mongos的cpu主要花在排序——resume token的对比,和document与bson之间的转换。
分片集群mongod火焰图: 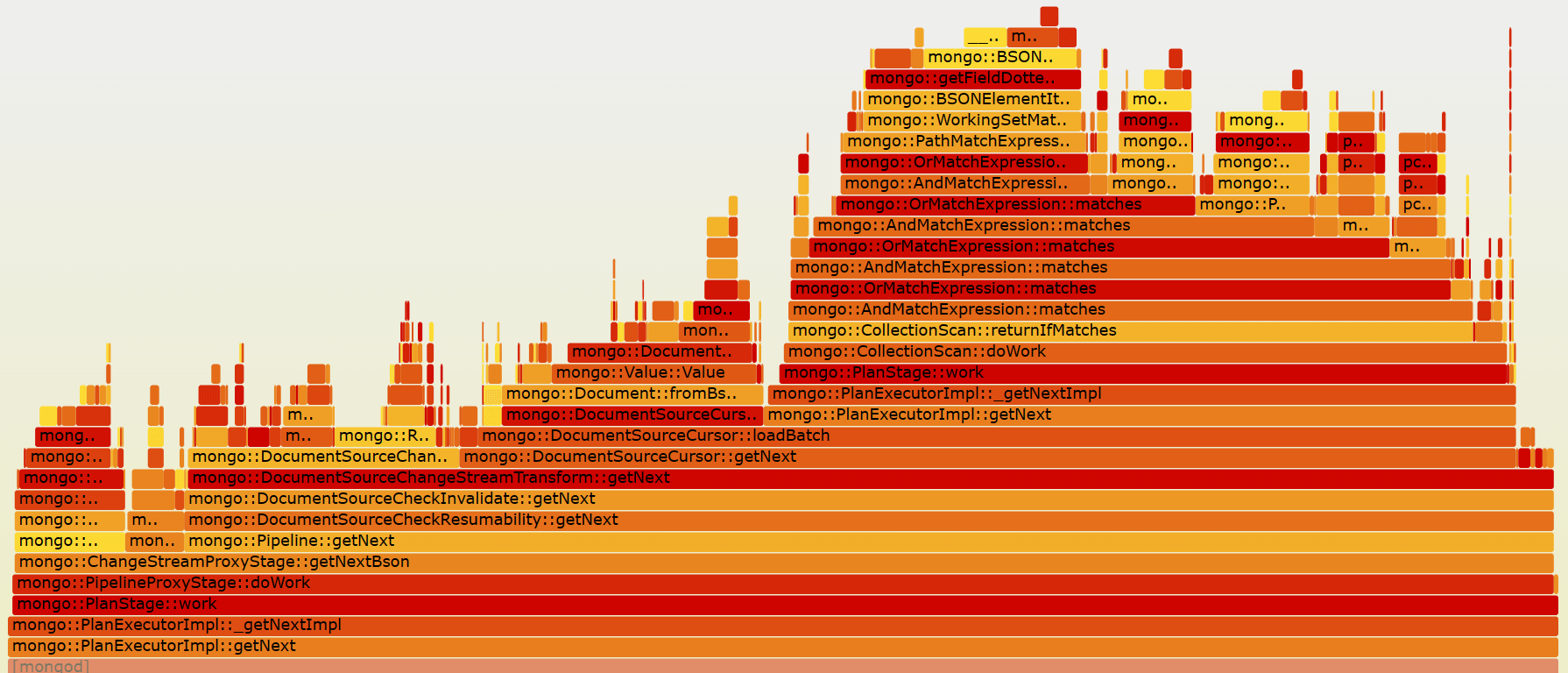 分片集群的mongod和副本集mongod一样,cpu主要花在match和transform。
分片集群的mongod和副本集mongod一样,cpu主要花在match和transform。
其他
4.2之前版本,$changeStream的read concern是majority,不能显式指定为其他。4.2及之后版本,可以使用其他read concern。
change stream请求是一定会发送到所有shard上的:
bool mustRunOnAllShards(const NamespaceString& nss, const LiteParsedPipeline& litePipe) {
// The following aggregations must be routed to all shards:
// - Any collectionless aggregation, such as non-localOps $currentOp.
// - Any aggregation which begins with a $changeStream stage.
return nss.isCollectionlessAggregateNS() || litePipe.hasChangeStream();
}
drop一个分布在多个shard上的collection,会收到对这个ns的多个drop事件——每个shard产生一个。
对driver发来的aggregate请求的处理
mongos上的explain结果:
也可以执行下面命令获取explain结果:
db.aggregate([{"$changeStream":{allChangesForCluster:true, startAtOperationTime:Timestamp({ t: 11, i: 0 })}}], {explain:true})
或者
db.runCommand({"aggregate":1, "pipeline":[{"$changeStream":{allChangesForCluster:true, startAtOperationTime:Timestamp({ t: 11, i: 0 })}}] , cursor:{}, explain:true})
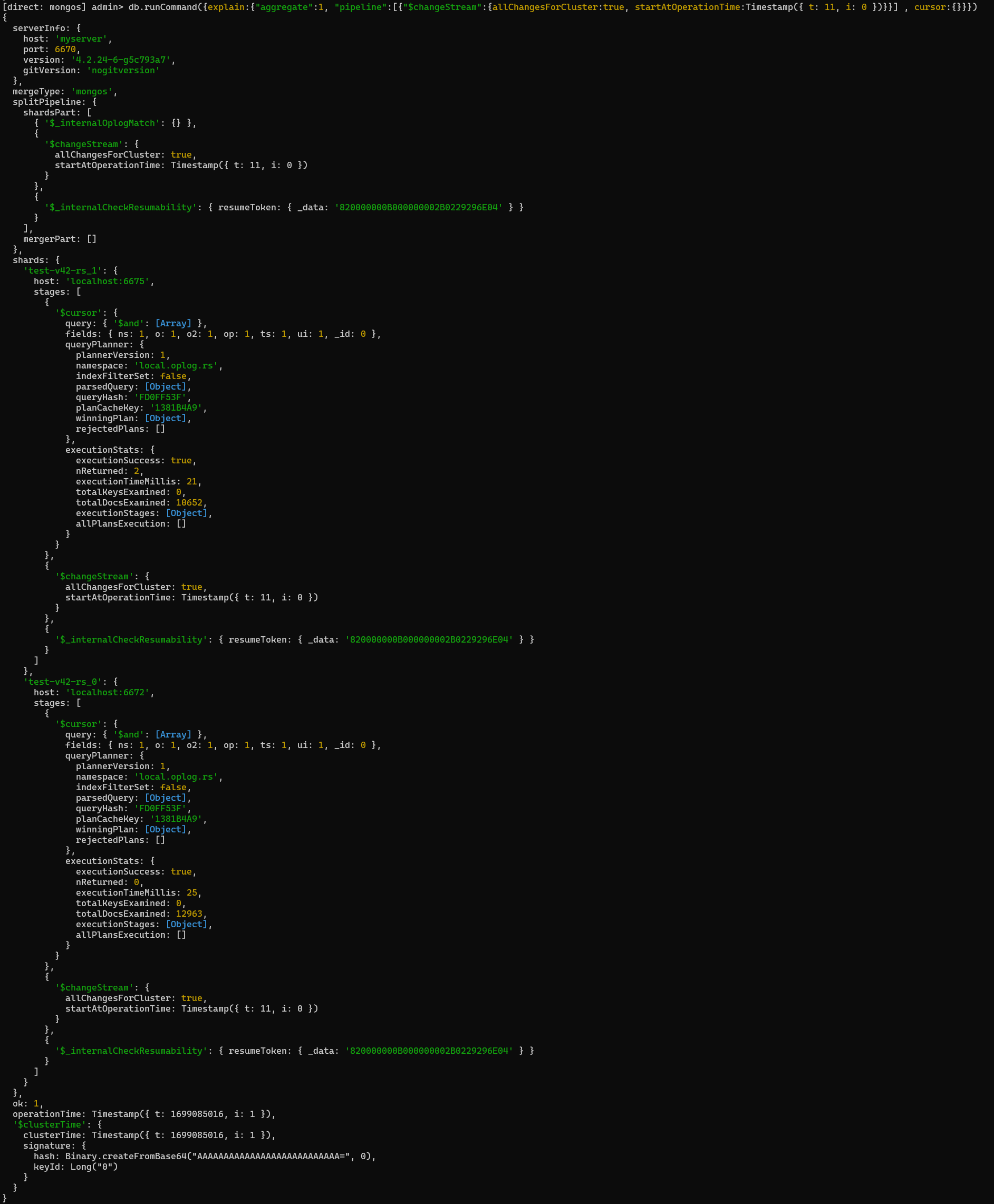 shards字段是每个shard上的执行计划,里面有一些被折叠没有显示的Array、Object,在mongod章节介绍。
shards字段是每个shard上的执行计划,里面有一些被折叠没有显示的Array、Object,在mongod章节介绍。
正则表达式
static constexpr StringData kRegexAllCollections = R"((?!(\$|system\.)))"_sd;
(?!pattern) 的形式叫做 零宽负向先行断言(zero-width negative lookahead assertion)。
| 表示某位置的字符串不能满足pattern。比如 admin.((?!($ | system.))),admin.$和admin.system.都不符合要求。 |