从一个例子开始
| Time | Client1 | Client2 |
|---|---|---|
| t0 | create Collection C0 | |
| t2 | search on C0 | |
| t4 | insert A1 into C0 | |
| t6 | search on C0 | |
| t8 | insert A2 into C0 | |
| t10 | search on C0 | |
| t12 | delete A1 from C0 | |
| t14 | search on C0 |
预期结果:
-
t2时刻,Client2应该看到C0是空表
-
t6时刻,Client2只能看到数据A1
-
t10时刻,Client2可以看到A1、A2
-
t14时刻,Client2只能看到A2
在单机场景里,这一切看起来理所当然。但是在分布式系统中,比如Milvus中,至少需要解决以下问题:
-
对事件顺序达成共识。Client1、Client2和Server如果位于不同的节点,它们的本地时钟没有完全同步。比如Client2比Client1的时钟慢一个小时,那么Client2只能看到Client1一个小时前写的数据显然不合理。
-
按顺序处理事件。比如t14时刻,预期Client2只能看到A2,如何确保t0、t4、t8、t12的Client1事件在集群内已经处理完?
Milvus 1.x版本只支持最终一致性,写入数据是异步的。比如Client1写入一条数据之后,Client2不确定会在什么时候能读到这个数据,但承诺一定会读到。
为了解决这些问题,Milvus 2.x 引入了一套基于全局时间戳(Timestamp)和水位线(Watermark)的机制,从而实现了多种可调的一致性等级。这套机制的核心,便是 Timestamp Oracle (TSO) 和 TimeTick。
Timestamp Oracle(TSO)
| 方案 | 原理 | 一致性语义 | 优点 | 缺点 | 典型系统 | 延迟/吞吐 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSO | 中心服务发放全局单调时间戳,支持批量 | 全局单调;适配快照隔离/MVCC | 语义清晰;工程成熟;跨分片统一时间线 | 中心/领导瓶颈;无法多节点同时提供服务 | TiDB/TiKV、Milvus | 中等延迟;吞吐可批量扩展 |
| TrueTime | 原子钟提供不确定区间;提交执行 commit-wait | 外部一致(与真实时间一致) | 最强时间语义;跨地域强一致 | 硬件依赖重;提交等待开销 | Google Spanner | 延迟较高;吞吐受 commit-wait 影响 |
| HLC | 物理时钟+逻辑时钟融合; | 因果一致+单调;非外部一致 | 去中心化;低延迟;容忍时钟漂移 | 读写冲突可能重试;时间非严格真实 | CockroachDB/MongoDB | 低延迟;高吞吐 |
| Sequencer/原子广播(Paxos/Raft) | 共识形成全序日志/编号,按同一顺序执行 | 线性一致的全序事件流 | 不依赖物理时钟;顺序语义强 | 领导/共识瓶颈;跨地域 RTT 高 | etcd/Raft | 延迟中高;吞吐受共识限制 |
像TiKV一样,Milvus也使用TSO的方案解决“顺序共识”问题,其核心职责是为集群中所有需要定序的事件(如 DML、DDL 操作)分配一个全局唯一且严格单调递增的时间戳。准确来说是TSO + HLC的方案,TSO为主,HLC为辅。Milvus采用的也是TiKV的实现。TiKV使用TSO,是因为它采用了Percolator事务模型,而TSO是Percolator的一个重要组成部分。
更准确地说,Milvus同时使用了TSO、HLC、Raft三种方案,只不过Raft被“封装”到了etcd里面,将其当作线性一致的stable storage。
整体架构
在 Milvus 中,TSO 的中心化授时服务由 RootCoord 的 active 实例承担。开启active&standby之后,root coord使用抢锁+租约方案来选出active,standby节点watch 删除事件,租约过期后尝试抢锁成为active。
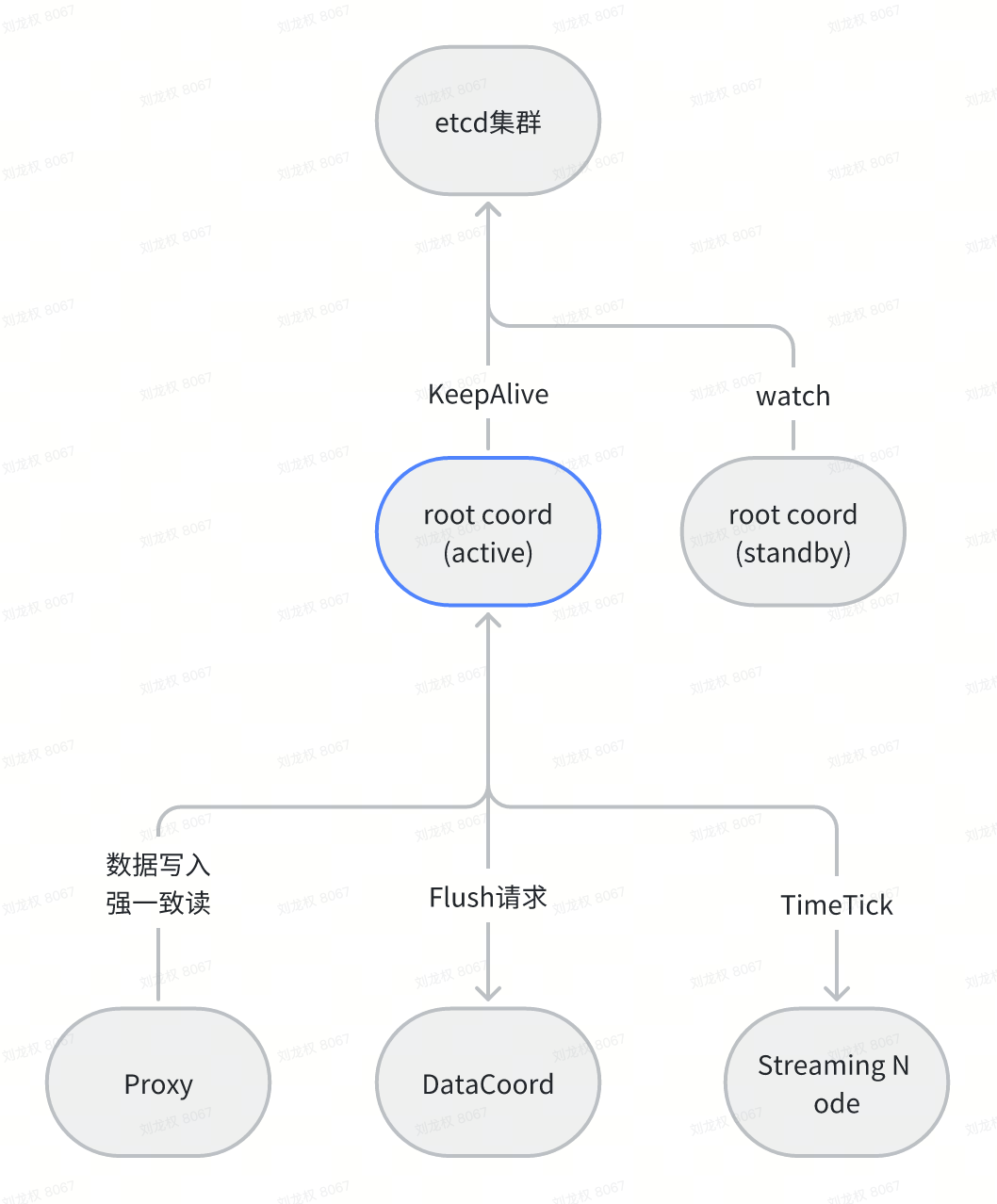
QueryCoord、IndexCoord、DataNode 等组件不直接分配 TSO,它们消费由上游带时间戳的数据或依赖 TimeTick 水位进行调度与可见性控制。
具体实现
TSO模块的实现主要考虑以下几点:
- 保证分配出去的时间戳严格单调递增。
-
单机场景没有问题
-
重点关注leader切换场景
-
- 高性能。主要使用以下两种优化:
-
预分配 preallocating
-
批量获取 batching
-
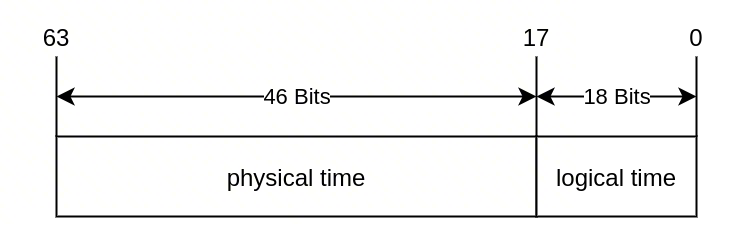
TSO分配的时间戳格式如下:
-
physical time是毫秒级的unix timestamp
-
logical time是一个从0递增的counter
初始化
初始化主要有以下工作:
-
读取已分配(包括预分配)的最大时间戳。预防时间戳回退
-
预分配三秒的时间戳,并记录到etcd。
-
更新内存中预分配的时间戳窗口。
func (t *timestampOracle) InitTimestamp() error {
// 从etcd中读取“已分配”的最大时间戳
last, err := t.loadTimestamp()
if err != nil {
return err
}
next := time.Now()
// next = max(time.now(), etcdSavedTs + 1ms) 保证单调递增
if typeutil.SubTimeByWallClock(next, last) < updateTimestampGuard {
next = last.Add(updateTimestampGuard)
}
// 预分配3秒的时间戳,saveInterval是硬编码——3s
save := next.Add(t.saveInterval)
// 更新etcd和内存值
if err := t.saveTimestamp(save); err != nil {
return err
}
log.Info("sync and save timestamp", zap.Time("last", last), zap.Time("save", save), zap.Time("next", next))
current := &atomicObject{
physical: next,
}
// atomic unsafe pointer
/* #nosec G103 */
atomic.StorePointer(&t.TSO, unsafe.Pointer(current))
// 之后,[next, save]之间的时间戳分配完全走内存
return nil
}
func (t *timestampOracle) saveTimestamp(ts time.Time) error {
// we use big endian here for compatibility issues
data := typeutil.Uint64ToBytesBigEndian(uint64(ts.UnixNano()))
err := t.txnKV.Save(context.TODO(), t.key, string(data))
if err != nil {
return errors.WithStack(err)
}
t.lastSavedTime.Store(ts)
return nil
}
时间戳分配
rootcoord的alloc timestamp接口最后调用的是GenerateTSO。
func (gta *GlobalTSOAllocator) GenerateTSO(count uint32) (uint64, error) {
var physical, logical int64
if count == 0 {
return 0, errors.New("tso count should be positive")
}
maxRetryCount := 10
for i := 0; i < maxRetryCount; i++ {
// 取出预分配窗口的左边界
current := (*atomicObject)(atomic.LoadPointer(>a.tso.TSO))
if current == nil || current.physical.Equal(typeutil.ZeroTime) {
// If it's leader, maybe SyncTimestamp hasn't completed yet
log.Info("sync hasn't completed yet, wait for a while")
time.Sleep(200 * time.Millisecond)
continue
}
physical = current.physical.UnixMilli()
// logical部分原子递增
logical = atomic.AddInt64(¤t.logical, int64(count))
// 如果左边界的logical超过了最大值 int64(1 << 18),就等待physical递增
if logical >= maxLogical && gta.LimitMaxLogic {
log.Info("logical part outside of max logical interval, please check ntp time",
zap.Int("retry-count", i))
// 等待50ms
time.Sleep(UpdateTimestampStep)
continue
}
return tsoutil.ComposeTS(physical, logical), nil
}
return 0, errors.New("can not get timestamp")
}
-
原子操作
-
logical递增
-
批量分配时间戳
physical递增
rootcoord启动的时候,会启动一个后台线程tsLoop。
func (c *Core) startServerLoop() {
c.wg.Add(1)
go c.tsLoop()
if !streamingutil.IsStreamingServiceEnabled() {
c.wg.Add(2)
go c.startTimeTickLoop()
go c.chanTimeTick.startWatch(&c.wg)
}
}
tsLoop 周期性地调用UpdateTSO。 推进physical。
func (c *Core) tsLoop() {
defer c.wg.Done()
// 每50ms推进一次physical
tsoTicker := time.NewTicker(tso2.UpdateTimestampStep)
defer tsoTicker.Stop()
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(c.ctx)
defer cancel()
log := log.Ctx(c.ctx)
for {
select {
case <-tsoTicker.C:
if err := c.tsoAllocator.UpdateTSO(); err != nil {
log.Warn("failed to update tso", zap.Error(err))
continue
}
ts := c.tsoAllocator.GetLastSavedTime()
metrics.RootCoordTimestampSaved.Set(float64(ts.Unix()))
case <-ctx.Done():
log.Info("rootcoord's ts loop quit!")
return
}
}
}
为什么是50ms?根据tikv的说法,etcd client重试间隔是25ms // Etcd client retry with
roundRobinQuorumBackoff(https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/blob/d62cdeee4863001b09e772ed013eb1342a1d0f89/client/v3/client.go#L488), // whose default interval is 25ms, so we sleep 50ms here. (https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/blob/d62cdeee4863001b09e772ed013eb1342a1d0f89/client/v3/options.go#L53)
UpdateTimestamp会判断左边界的physical部分和右边界是否需要更新。physical部分与物理时间并不完全对应。
func (t *timestampOracle) UpdateTimestamp() error {
// 取出窗口左边界
prev := (*atomicObject)(atomic.LoadPointer(&t.TSO))
now := time.Now()
jetLag := typeutil.SubTimeByWallClock(now, prev.physical)
if jetLag > 3*UpdateTimestampStep {
log.Ctx(context.TODO()).WithRateGroup("tso", 1, 60).RatedWarn(60.0, "clock offset is huge, check network latency and clock skew", zap.Duration("jet-lag", jetLag),
zap.Time("prev-physical", prev.physical), zap.Time("now", now))
}
var next time.Time
prevLogical := atomic.LoadInt64(&prev.logical)
// If the system time is greater, it will be synchronized with the system time.
if jetLag > updateTimestampGuard {
// 需要更新physical
next = now
} else if prevLogical > maxLogical/2 {
// The reason choosing maxLogical/2 here is that it's big enough for common cases.
// Because there is enough timestamp can be allocated before next update.
log.Warn("the logical time may be not enough", zap.Int64("prev-logical", prevLogical))
next = prev.physical.Add(time.Millisecond)
} else {
// It will still use the previous physical time to alloc the timestamp.
// 左边界不需要递增
return nil
}
// 判断更新后的左边界是否超过了预分配窗口的右边界。如果超过则递增右边界。
// It is not safe to increase the physical time to `next`.
// The time window needs to be updated and saved to etcd.
if typeutil.SubTimeByWallClock(t.lastSavedTime.Load().(time.Time), next) <= updateTimestampGuard {
save := next.Add(t.saveInterval)
if err := t.saveTimestamp(save); err != nil {
return err
}
}
// 更新左边界
current := &atomicObject{
physical: next,
logical: 0,
}
// atomic unsafe pointer
/* #nosec G103 */
atomic.StorePointer(&t.TSO, unsafe.Pointer(current))
return nil
}
总结
- 保证分配出去的时间戳严格单调递增。
-
etcd的线性一致性
-
原子操作
-
leader切换时,新leader是新的窗口。如果leader频繁切换,导致时间窗口一直往后推进,与真实时间差别很大
-
- 高性能:
-
预分配 3秒的窗口,理论上可以分配出去
3 * 1000 * (1<< 18) = 78643万个时间戳,窗口内时间戳的分配完全走内存 -
如果qps特别高,把logical部分打满(一般不会,每50ms也会检测一次logical是否过半),则会主动sleep 50ms
-
窗口用完时,会重新向etcd预分配。大约每3秒访问一次etcd
-
支持批量获取时间戳
-
例子中的第一个问题得到了解决——“顺序的共识”。有了TSO,Milvus所有组件就可以判断任意两个事件的先后顺序,但是如何保证顺序处理事件呢?
TimeTick
为什么需要TimeTick
有了TSO,理论上可以完全按顺序处理事件,以保证一致性。比如,只能有一个proxy处理读写,严格按时间戳顺序写入消息到消息队列,但这样性能太低。当有多个proxy时,由于网络延迟的不确定性,发送到msg stream的消息不一定是按照时间戳顺序排列的。TimeTick就是来解决这个问题的。
类似raft的乱序提交优化
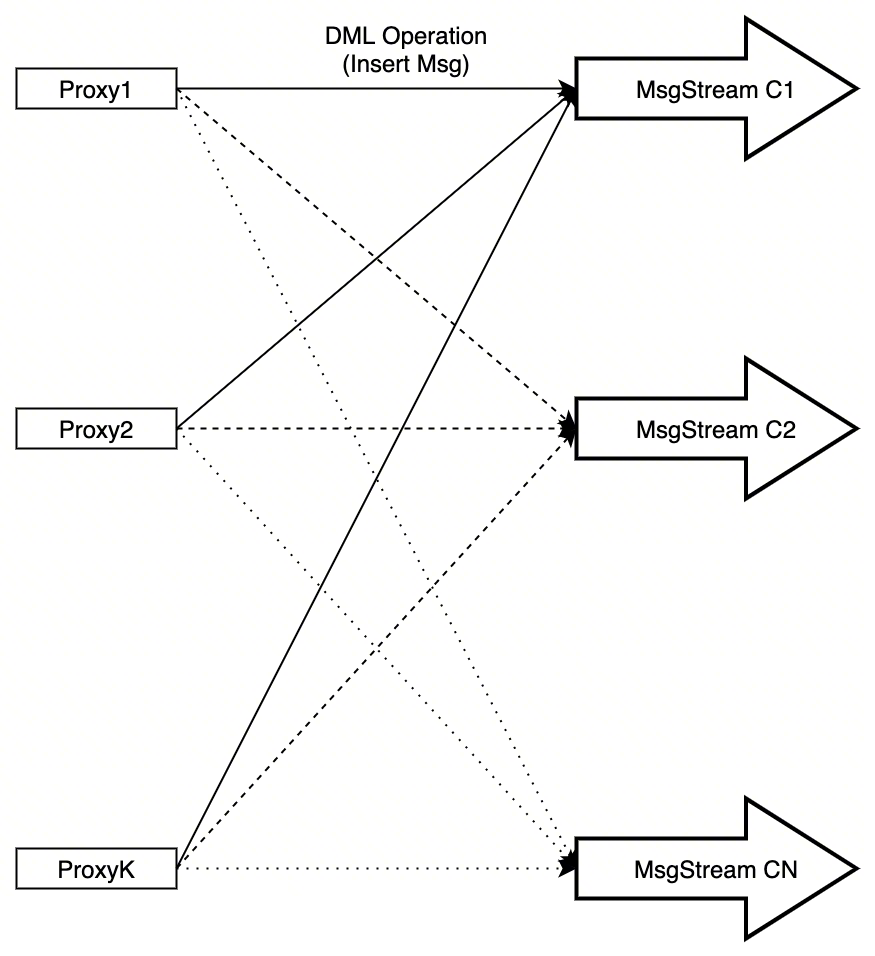
现实情况下,每个msg stream都会被多个proxy写入消息。proxy收到insert请求之后,会根据每个primary key的hash value,把数据拆成多份,分别投到不同的消息队列里。
// HashPK2Channels hash primary keys to channels
func HashPK2Channels(primaryKeys *schemapb.IDs, shardNames []string) []uint32 {
numShard := uint32(len(shardNames))
var hashValues []uint32
switch primaryKeys.IdField.(type) {
case *schemapb.IDs_IntId:
pks := primaryKeys.GetIntId().Data
for _, pk := range pks {
value, _ := Hash32Int64(pk)
hashValues = append(hashValues, value%numShard)
}
case *schemapb.IDs_StrId:
pks := primaryKeys.GetStrId().Data
for _, pk := range pks {
hash := HashString2Uint32(pk)
hashValues = append(hashValues, hash%numShard)
}
default:
// TODO::
}
return hashValues
}
所以,对于单个MsgStream来说,要想保持顺序,至少有两个并发会打乱顺序:
-
proxy间是并发的
-
proxy内对堆积任务的处理是并发的
但是,来自同一个Proxy的msg在趋势上,会按照时间戳顺序排列。 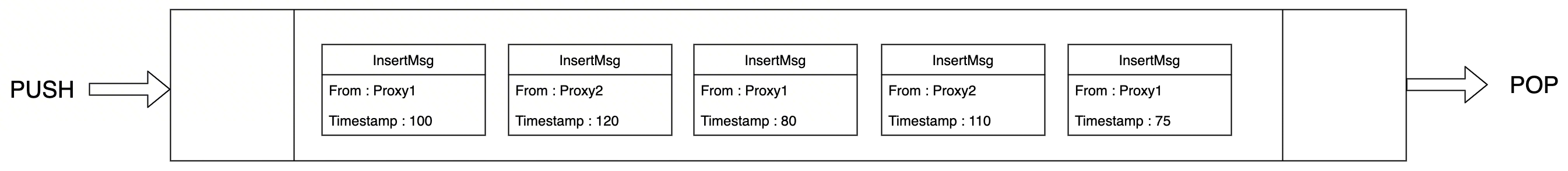
假设现在我想做一个写后读,那么如何确保我一定能读到刚写入的数据呢?
实现
总体思路: 把流数据分段,保证段与段之间是单调递增的——定期往每个pChannel里面写入”所有pChannel”的最小时间戳。
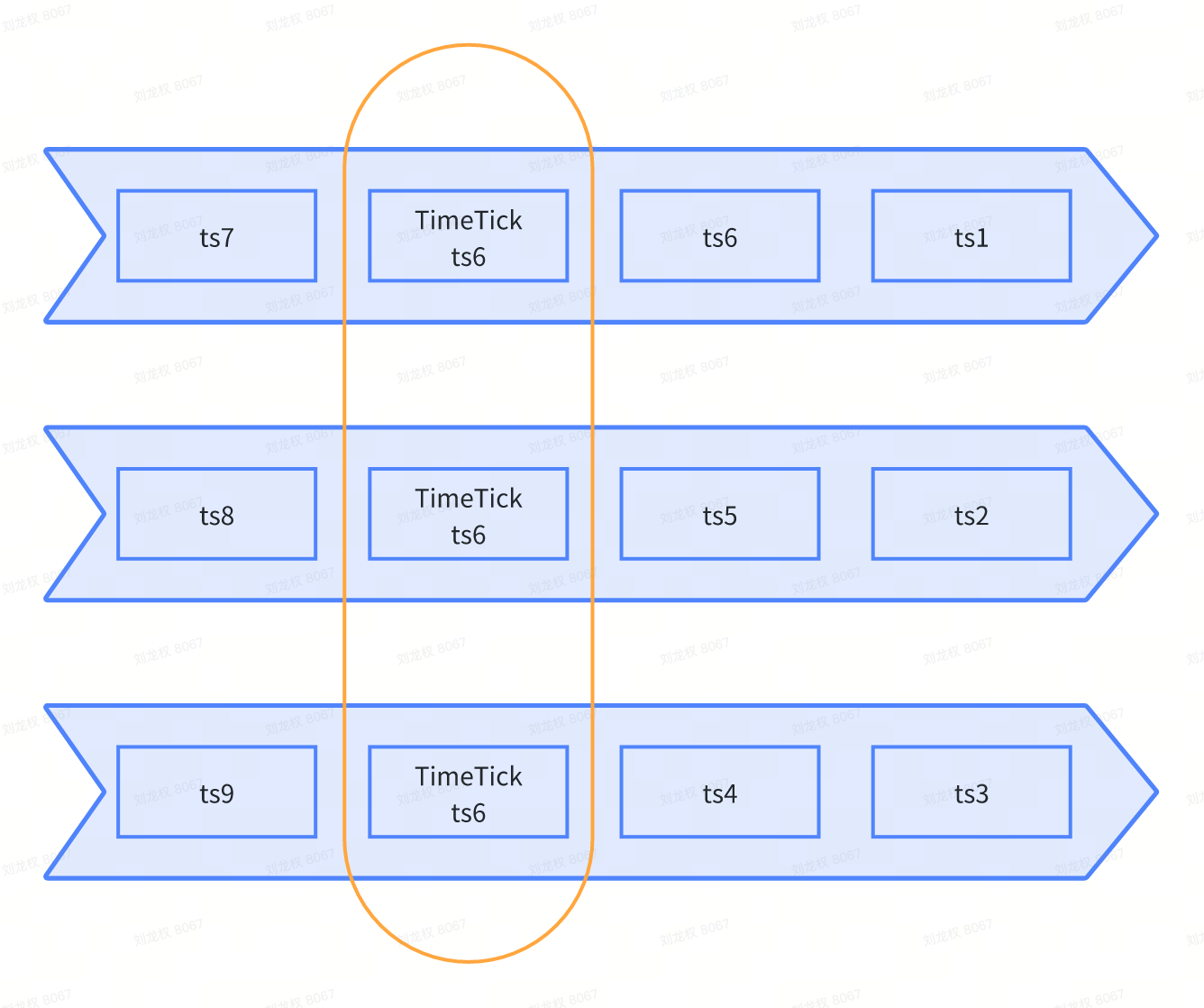
分工如下:
-
proxy维护统计信息。但是proxy并不真正去读msg stream获取最小时间戳(不容易实现),而是在任务调度中动态维护。
-
root coord汇总统计信息,并写入time tick消息。
proxy任务入队,并申请时间戳
proxy从root coord为每一个事件申请时间戳:
// dm、dd、dq任务入队都会走这里
func (queue *baseTaskQueue) Enqueue(t task) error {
err := t.OnEnqueue()
if err != nil {
return err
}
var ts Timestamp
var id UniqueID
// 只有非强一致的search和query,返回true
if t.CanSkipAllocTimestamp() {
ts = tsoutil.ComposeTS(time.Now().UnixMilli(), 0)
// 申请一个本地自增的id
id, err = globalMetaCache.AllocID(t.TraceCtx())
if err != nil {
return err
}
} else {
// 申请一个全局时间戳,走root coord接口
ts, err = queue.tsoAllocatorIns.AllocOne(t.TraceCtx())
if err != nil {
return err
}
// we always use same msg id and ts for now.
id = UniqueID(ts)
}
t.SetTs(ts)
t.SetID(id)
t.SetOnEnqueueTime()
return queue.addUnissuedTask(t)
}
另外需要特别关注的是,dm任务入队是加锁的:
func (queue *dmTaskQueue) Enqueue(t task) error {
...
queue.statsLock.Lock()
defer queue.statsLock.Unlock()
err = queue.baseTaskQueue.Enqueue(t)
if err != nil {
return err
}
pChannels := dmt.getChannels()
queue.commitPChanStats(dmt, pChannels)
...
}
目的是为了保证 申请时间戳+入队的原子性,也就是按照时间戳顺序排队等待执行。 dm的锁,是为了保证 “申请时间戳+入队+更新minTs” 的原子性,否则会有问题,比如: 有问题的例子:
-
当前minTs为0
-
事件1被分配时间戳 1
-
事件2被分配时间戳 2
-
使用事件2更新minTs,minTs此时为2
-
proxy上报minTs=2给root coord
-
使用事件1更新minTs,minTs此时为1
预期结果:
-
当前minTs为0
-
事件1被分配时间戳 1
-
使用事件1更新minTs,minTs此时为1
-
事件2被分配时间戳 2
-
使用事件2更新minTs,minTs此时为2
-
proxy上报minTs=2给root coord
func (queue *dmTaskQueue) commitPChanStats(dmt dmlTask, pChannels []pChan) {
// 1. prepare new stat for all pChannels
newStats := make(map[pChan]pChanStatistics)
beginTs := dmt.BeginTs()
endTs := dmt.EndTs()
// pChannels 是当前任务会用到的所有pChannel
for _, channel := range pChannels {
newStats[channel] = pChanStatistics{
minTs: beginTs,
maxTs: endTs,
}
}
// 2. update stats for all pChannels
for cName, newStat := range newStats {
currentStat, ok := queue.pChanStatisticsInfos[cName]
if !ok {
currentStat = &pChanStatInfo{
pChanStatistics: newStat,
tsSet: map[Timestamp]struct{}{
newStat.minTs: {},
},
}
queue.pChanStatisticsInfos[cName] = currentStat
} else {
if currentStat.minTs > newStat.minTs {
currentStat.minTs = newStat.minTs
}
if currentStat.maxTs < newStat.maxTs {
currentStat.maxTs = newStat.maxTs
}
currentStat.tsSet[newStat.minTs] = struct{}{}
}
}
}
也就是说,每个proxy维护当前“未发送至消息队列”的任务的统计信息——按pChannel维度维护最小时间戳。
proxy任务出队
任务完成后(用户收到响应),更新minTs:
-
当前的实现是记录调度器队列中所有任务的时间戳,并通过遍历的方式更新minTs
-
明显的优化是 使用“最小堆”计算minTs,时间度从 O(N) -> O(lgn)
func (queue *dmTaskQueue) popPChanStats(t task) {
channels := t.(dmlTask).getChannels()
taskTs := t.BeginTs()
for _, cName := range channels {
info, ok := queue.pChanStatisticsInfos[cName]
if ok {
delete(info.tsSet, taskTs)
if len(info.tsSet) <= 0 {
delete(queue.pChanStatisticsInfos, cName)
} else {
newMinTs := info.maxTs
for ts := range info.tsSet {
if newMinTs > ts {
newMinTs = ts
}
}
info.minTs = newMinTs
}
}
}
}
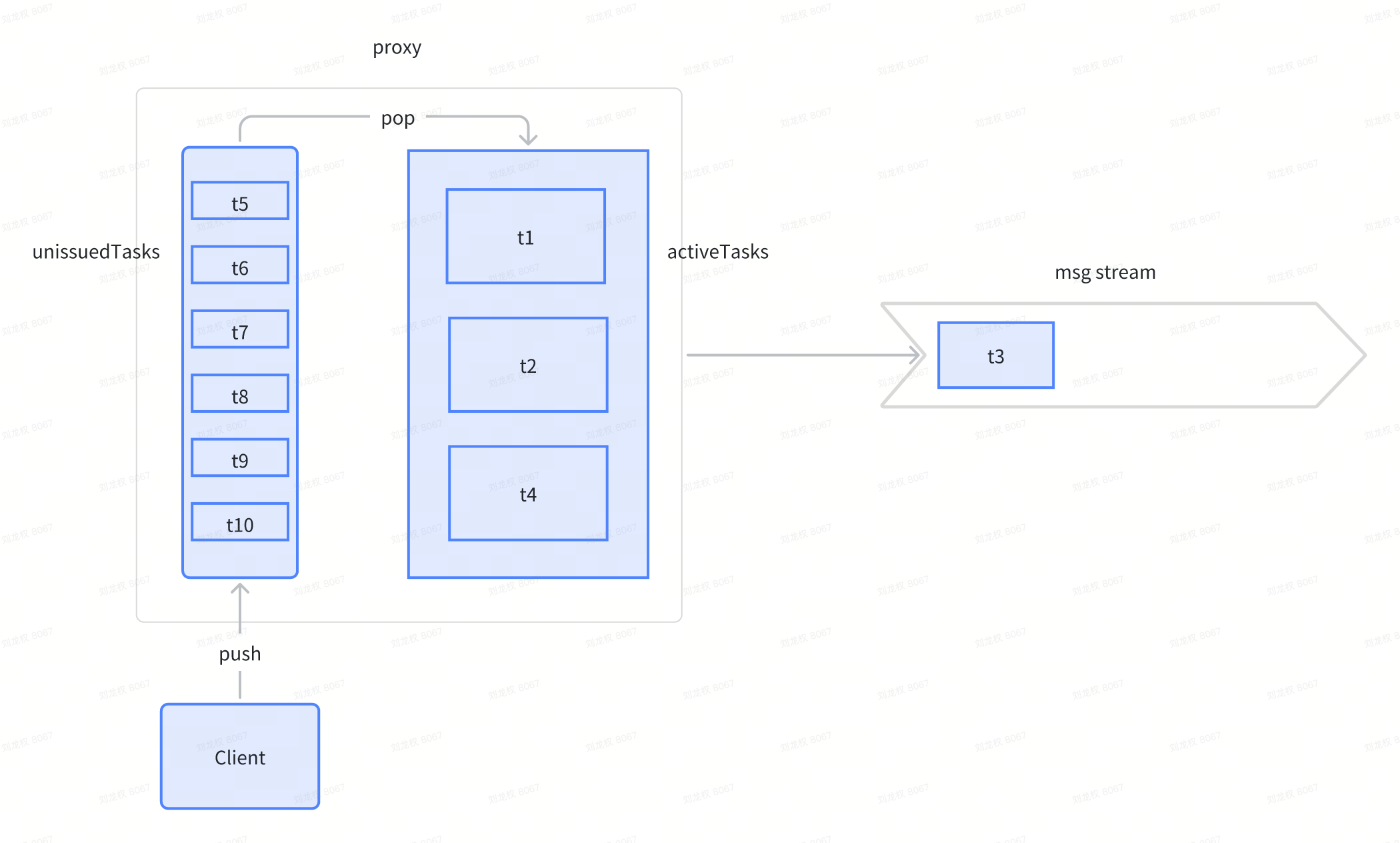
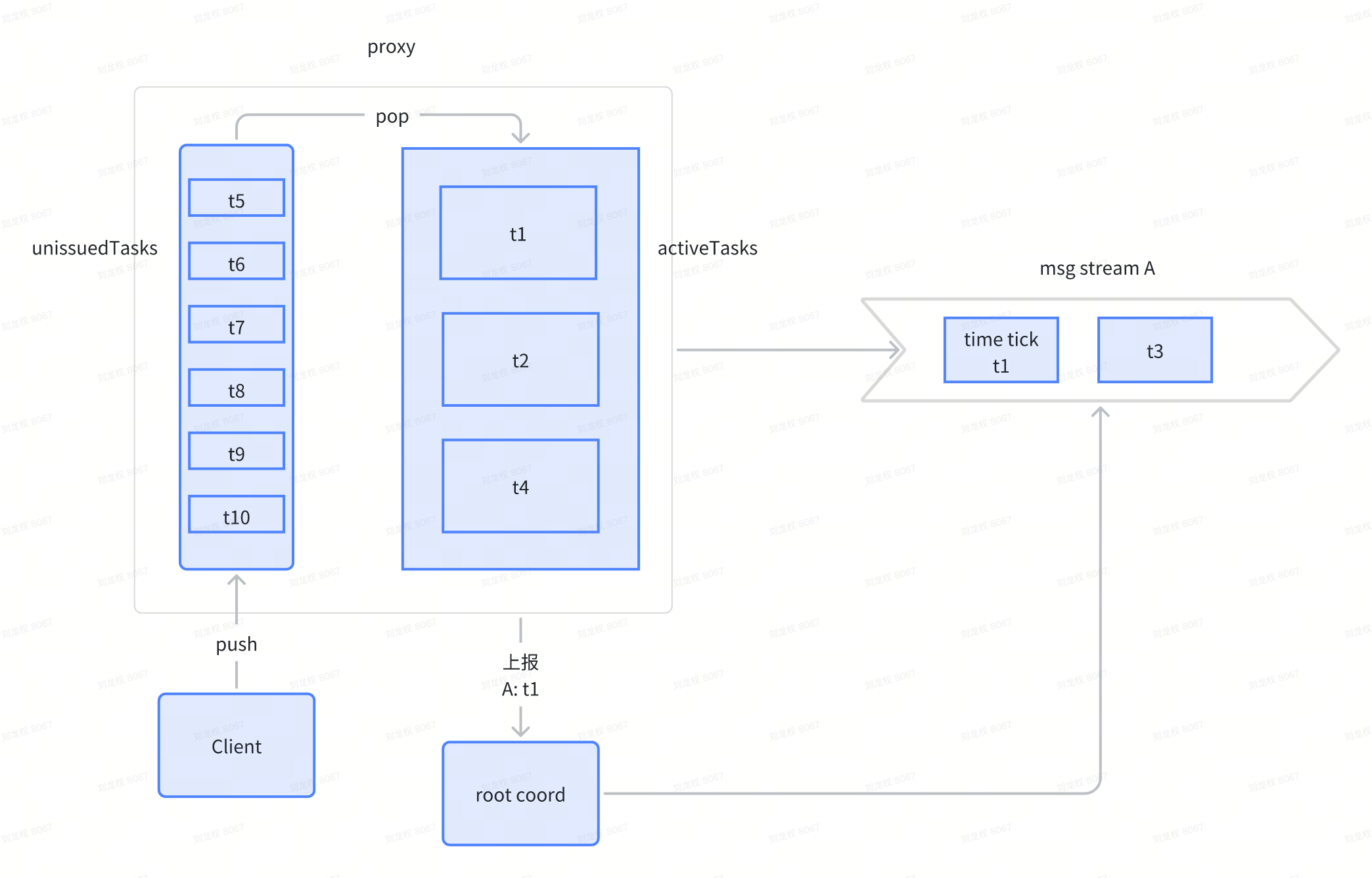
把入队、出队结合起来举个例子:
- 初始状态,proxy中没有任务需要处理,msg stream中也没有任何消息
- proxy收到t1~t10等消息。快速处理完了t3,并投到消息队列,t1、t2、t4还在active tasks中
- proxy上报每个pChannel的minTs给root coord,root coord写入time tick消息到msg stream
proxy上报时间戳
proxy有一个后台任务,周期性(默认100ms)更新所有pChannel的minTs,并向root coord上报。tick函数主要做两件事情:
-
减少minTs的抖动
-
防止minTs回退(理论上不会发生)
func (ticker *channelsTimeTickerImpl) tick() error {
now, err := ticker.tso.AllocOne(ticker.ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Warn("Proxy channelsTimeTickerImpl failed to get ts from tso", zap.Error(err))
return err
}
stats, err2 := ticker.getStatisticsFunc()
if err2 != nil {
log.Warn("failed to get tt statistics", zap.Error(err))
return nil
}
ticker.statisticsMtx.Lock()
defer ticker.statisticsMtx.Unlock()
ticker.defaultTimestamp = now
minTs := now
for pchan := range ticker.currents {
current := ticker.currents[pchan]
stat, ok := stats[pchan]
if !ok {
delete(ticker.minTsStatistics, pchan)
delete(ticker.currents, pchan)
} else {
if stat.minTs > current {
ticker.minTsStatistics[pchan] = stat.minTs - 1
next := now + Timestamp(Params.ProxyCfg.TimeTickInterval.GetAsDuration(time.Millisecond))
if next > stat.maxTs {
next = stat.maxTs
}
ticker.currents[pchan] = next
}
lastMin := ticker.minTsStatistics[pchan]
if minTs > lastMin {
minTs = lastMin
}
}
}
for pchan, value := range stats {
if value.minTs == typeutil.ZeroTimestamp {
log.Warn("channelsTimeTickerImpl.tick, stats contains physical channel which min ts is zero ",
zap.String("pchan", pchan))
continue
}
_, ok := ticker.currents[pchan]
if !ok {
ticker.minTsStatistics[pchan] = value.minTs - 1
ticker.currents[pchan] = now
}
if minTs > value.minTs-1 {
minTs = value.minTs - 1
}
}
ticker.minTimestamp = minTs
return nil
}
proxy还有一个后台任务,周期性(默认100ms)调用rootCoord.UpdateChannelTimeTick上报所有的pChannel的minTs
// Start starts a proxy node.
func (node *Proxy) Start() error {
...
if !streamingutil.IsStreamingServiceEnabled() {
// 启动后台任务,周期性更新minTs
if err := node.chTicker.start(); err != nil {
log.Warn("failed to start channels time ticker", zap.String("role", typeutil.ProxyRole), zap.Error(err))
return err
}
log.Debug("start channels time ticker done", zap.String("role", typeutil.ProxyRole))
// 周期性调用rootCoord.UpdateChannelTimeTick,上报minTs
node.sendChannelsTimeTickLoop()
}
...
}
root coord汇总并写入TimeTick消息
Root coord启动时会启动两个后台任务:
- startTimeTickLoop是周期性地收集ddl的minTs,并像proxy一样发送ChannelTimeTickMsg消息(不走rpc)
-
dd任务是由proxy直接rpc调用root coord发送的。root coord维护了dd任务的minTs,为什么不在proxy侧做?因为root coord会做一些不经过proxy的延迟gc任务,比如drop collection和drop partition。
-
minDdlTs的维护使用小顶堆,入队、出队的时候都更新minDdlTs
-
- root coord收集到ddl以及所有proxy的UpdateChannelTimeTick消息之后,触发一次发送TimeTick消息(非定时任务)。
- 取所有pChannel的最小minTs发送给每一个pChannel,即使这个pChannel没有任何流量
func (c *Core) startServerLoop() {
c.wg.Add(1)
// 周期性推进physical及预分配窗口
go c.tsLoop()
if !streamingutil.IsStreamingServiceEnabled() {
c.wg.Add(2)
go c.startTimeTickLoop() // 每100ms调用一次sendMinDdlTsAsTt
go c.chanTimeTick.startWatch(&c.wg) // 收到所有session的UpdateChannelTimeTick消息后,发送tt消息到消息队列
}
}
func (c *Core) sendMinDdlTsAsTt() {
if !paramtable.Get().CommonCfg.TTMsgEnabled.GetAsBool() {
return
}
log := log.Ctx(c.ctx)
code := c.GetStateCode()
if code != commonpb.StateCode_Healthy {
log.Warn("rootCoord is not healthy, skip send timetick")
return
}
minBgDdlTs := c.ddlTsLockManager.GetMinDdlTs()
minNormalDdlTs := c.scheduler.GetMinDdlTs()
minDdlTs := funcutil.Min(minBgDdlTs, minNormalDdlTs)
// zero -> ddlTsLockManager and scheduler not started.
if minDdlTs == typeutil.ZeroTimestamp {
log.Warn("zero ts was met, this should be only occurred in starting state", zap.Uint64("minBgDdlTs", minBgDdlTs), zap.Uint64("minNormalDdlTs", minNormalDdlTs))
return
}
// max -> abnormal case, impossible.
if minDdlTs == typeutil.MaxTimestamp {
log.Warn("ddl ts is abnormal, max ts was met", zap.Uint64("minBgDdlTs", minBgDdlTs), zap.Uint64("minNormalDdlTs", minNormalDdlTs))
return
}
if err := c.sendTimeTick(minDdlTs, "timetick loop"); err != nil {
log.Warn("failed to send timetick", zap.Error(err))
}
}
如果启用了Streaming Service,则由streamingnode处理time tick。AckManager和timeTickSyncOperator。
root coord维护了所有proxy的session。只要有任意一个proxy没有发送update time tick消息,root coord就不会生成TimeTick消息。
总结
有了TimeTick逻辑之后,root coord就会周期性地往消息队列中写入time tick消息。time tick是一种watermark,也可以看作是一种对消费者的承诺——后面事件的时间戳均大于此time tick消息的时间戳。
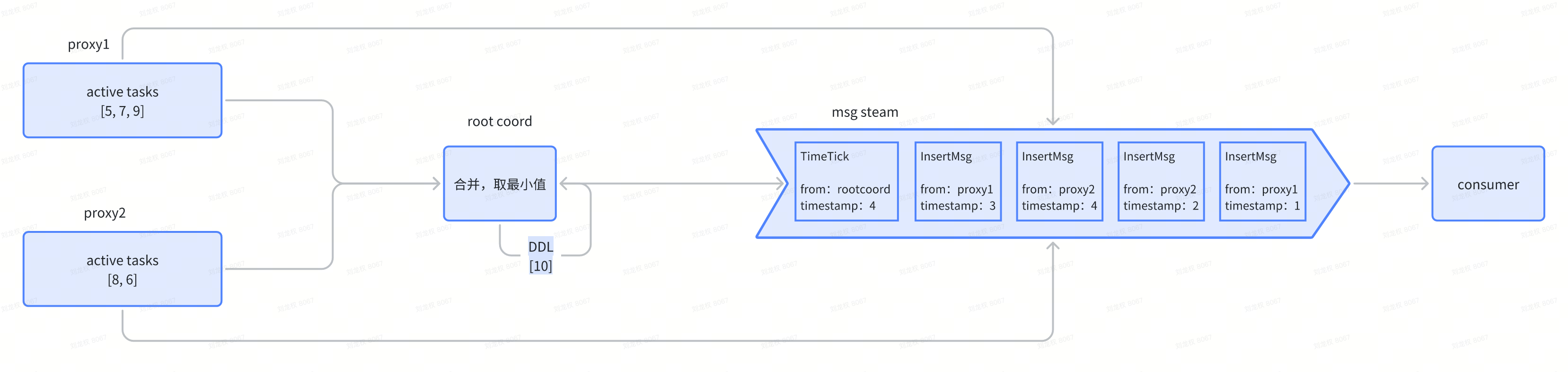
对于Milvus来说,pChannel就是topic,每个topic都只有一个partition,所以每次对每个topic只需要发送一个TimeTick消息。如果Topic有多个partition(Milvus不允许),则需要向每个partition都发送TimeTick消息。
这样,前面例子提到的第二个问题也解决了。这里讲的是TimeTick的生成逻辑,下面讲一下TimeTick的消费逻辑,两者共同构成了Milvus的一致性实现。
一致性实现
概述
QueryNodes 会不断从消息队列里面拿到Insert、Delete等消息以及TimeTick消息,每消费到一个TimeTick,QueryNodes 会把这个时间戳称为可服务时间——“ServiceTime”。ServiceTime的含义就是QueryNodes 能够看到之前所有的数据了。 Milvus 根据不同用户对一致性以及可用性的需求,提供了 GuaranteeTs,用户可以指定GuaranteeTs 告知 QueryNodes 我这次 Search 请求必须看到 GuaranteeTs 以前的所有数据。 又根据GuaranteeTs和ServiceTime的关系,Milvus抽象出了不同的一致性等级。
-
强一致:使用最新的时间戳作为GuaranteeTs,可以看到最新的数据
-
会话一致:客户端插入数据的最新时间戳被用作 GuaranteeTs,可以看到自己的最新写入
-
有界一致:GuranteeTs 设置为比当前时间(非时间戳)更早的时间点(默认5s)
-
最终一致:GuaranteeTs 设置为-1,以跳过一致性检查,立即执行搜索请求
type ConsistencyLevel int32
const (
ConsistencyLevel_Strong ConsistencyLevel = 0
ConsistencyLevel_Session ConsistencyLevel = 1 // default in PyMilvus
ConsistencyLevel_Bounded ConsistencyLevel = 2
ConsistencyLevel_Eventually ConsistencyLevel = 3
ConsistencyLevel_Customized ConsistencyLevel = 4 // Users pass their own `guarantee_timestamp`.
)
func parseGuaranteeTsFromConsistency(ts, tMax typeutil.Timestamp, consistency commonpb.ConsistencyLevel) typeutil.Timestamp {
switch consistency {
case commonpb.ConsistencyLevel_Strong:
ts = tMax
case commonpb.ConsistencyLevel_Bounded:
ratio := Params.CommonCfg.GracefulTime.GetAsDuration(time.Millisecond)
ts = tsoutil.AddPhysicalDurationOnTs(tMax, -ratio)
case commonpb.ConsistencyLevel_Eventually:
ts = 1
}
return ts
}
func (t *searchTask) CanSkipAllocTimestamp() bool {
// get consistencyLevel from request or collection
return consistencyLevel != commonpb.ConsistencyLevel_Strong
}
Query node实现
-
维护自身的ServiceTime
-
收到搜索请求时,对比GuaranteeTs与自己的ServiceTime
-
如果GuaranteeTs > ServiceTime,等待ServiceTime推进
-
如果GuaranteeTs <= ServiceTime,执行搜索请求
-
实现分几个层次:
-
Mq client模块消费所有topic并缓存
-
后台任务消费消息推进ServiceTime
-
搜索请求等待ServiceTime推进
Mq client模块
Query node启动时,会拉起bufMsgPackToChannel后台任务,负责消费所有topic。
bufMsgPackToChannel函数:
-
并行读取所有topic的消息,直到所有topic的TimeTick ts对齐,期间的消息全部被缓存起来
-
如果当前消费进度比较落后,则会多缓存几批数据,一起返回出去
func (ms *MqTtMsgStream) bufMsgPackToChannel() {
chanTtMsgSync := make(map[mqwrapper.Consumer]bool)
for {
select {
case <-ms.ctx.Done():
return
default:
timeTickBuf := make([]TsMsg, 0)
startBufTime := time.Now()
var endTs uint64
var size uint64
var containsEndBufferMsg bool
// continueBuffering包含“消费进度落后多攒消息”的自适应逻辑
for ms.continueBuffering(endTs, size, startBufTime) && !containsEndBufferMsg {
ms.consumerLock.Lock()
// wait all channels get ttMsg
for _, consumer := range ms.consumers {
if !chanTtMsgSync[consumer] {
ms.chanWaitGroup.Add(1)
go ms.consumeToTtMsg(consumer)
}
}
ms.chanWaitGroup.Wait()
// block here until all channels reach same timetick
currTs, ok := ms.allChanReachSameTtMsg(chanTtMsgSync)
if !ok || currTs <= ms.lastTimeStamp {
ms.consumerLock.Unlock()
continue
}
endTs = currTs
}
// skip endTs = 0 (no run for ctx error)
if endTs > 0 {
msgPack := MsgPack{
BeginTs: ms.lastTimeStamp,
EndTs: endTs,
Msgs: uniqueMsgs,
StartPositions: lo.MapToSlice(startPositions, func(_ string, pos *msgpb.MsgPosition) *msgpb.MsgPosition { return pos }),
EndPositions: lo.MapToSlice(endPositions, func(_ string, pos *msgpb.MsgPosition) *msgpb.MsgPosition { return pos }),
}
select {
case ms.receiveBuf <- &msgPack:
case <-ms.ctx.Done():
return
}
ms.lastTimeStamp = endTs
}
}
}
}
在把消息交给query node上层逻辑之前,还会把消息按照vchannel分好。同时根据topic的时间戳设置所有vchannel的时间戳,保证vchannel没有消息也能推进。
func (d *Dispatcher) groupingMsgs(pack *MsgPack) map[string]*MsgPack {
// init packs for all targets, even though there's no msg in pack,
// but we still need to dispatch time ticks to the targets.
targetPacks := make(map[string]*MsgPack)
d.targets.Range(func(vchannel string, t *target) bool {
targetPacks[vchannel] = &MsgPack{
BeginTs: pack.BeginTs,
EndTs: pack.EndTs,
Msgs: make([]msgstream.TsMsg, 0),
StartPositions: pack.StartPositions,
EndPositions: pack.EndPositions,
}
return true
})
// group messages by vchannel
for _, msg := range pack.Msgs {
var vchannel, collectionID string
switch msg.Type() {
case commonpb.MsgType_Insert:
vchannel = msg.(*msgstream.InsertMsg).GetShardName()
case commonpb.MsgType_Delete:
vchannel = msg.(*msgstream.DeleteMsg).GetShardName()
case commonpb.MsgType_CreateCollection:
collectionID = strconv.FormatInt(msg.(*msgstream.CreateCollectionMsg).GetCollectionID(), 10)
case commonpb.MsgType_DropCollection:
collectionID = strconv.FormatInt(msg.(*msgstream.DropCollectionMsg).GetCollectionID(), 10)
case commonpb.MsgType_CreatePartition:
collectionID = strconv.FormatInt(msg.(*msgstream.CreatePartitionMsg).GetCollectionID(), 10)
case commonpb.MsgType_DropPartition:
collectionID = strconv.FormatInt(msg.(*msgstream.DropPartitionMsg).GetCollectionID(), 10)
}
if vchannel == "" {
// we need to dispatch it to the vchannel of this collection
for k := range targetPacks {
if !strings.Contains(k, collectionID) {
continue
}
// TODO: There's data race when non-dml msg is sent to different flow graph.
// Wrong open-trancing information is generated, Fix in future.
targetPacks[k].Msgs = append(targetPacks[k].Msgs, msg)
}
continue
}
if _, ok := targetPacks[vchannel]; ok {
targetPacks[vchannel].Msgs = append(targetPacks[vchannel].Msgs, msg)
}
}
return targetPacks
}
ServiceTime的推进
Query node对于每个collection的每个vchannel都有一个pipeline处理到来的消息。
Pipeline总是以deleteNode结尾,所以deleteNode就负责推进ServiceTime。
func NewPipeLine(
collection *Collection,
channel string,
manager *DataManager,
dispatcher msgdispatcher.Client,
delegator delegator.ShardDelegator,
) (Pipeline, error) {
// skip add embedding node when collection has no function.
if embeddingNode != nil {
p.Add(filterNode, embeddingNode, insertNode, deleteNode)
} else {
p.Add(filterNode, insertNode, deleteNode)
}
return p, nil
}
func (dNode *deleteNode) Operate(in Msg) Msg {
metrics.QueryNodeWaitProcessingMsgCount.WithLabelValues(fmt.Sprint(paramtable.GetNodeID()), metrics.DeleteLabel).Dec()
nodeMsg := in.(*deleteNodeMsg)
if len(nodeMsg.deleteMsgs) > 0 {
// partition id = > DeleteData
deleteDatas := make(map[UniqueID]*delegator.DeleteData)
for _, msg := range nodeMsg.deleteMsgs {
dNode.addDeleteData(deleteDatas, msg)
}
// do Delete, use ts range max as ts
dNode.delegator.ProcessDelete(lo.Values(deleteDatas), nodeMsg.timeRange.timestampMax)
}
// update tSafe
dNode.delegator.UpdateTSafe(nodeMsg.timeRange.timestampMax)
return nil
}
// updateTSafe read current tsafe value from tsafeManager.
func (sd *shardDelegator) UpdateTSafe(tsafe uint64) {
sd.tsCond.L.Lock()
if tsafe > sd.latestTsafe.Load() {
sd.latestTsafe.Store(tsafe)
sd.tsCond.Broadcast()
}
sd.tsCond.L.Unlock()
}
搜索请求等待ServiceTime推进
shardDelegator在做search之前,先调用waitTSafe
// waitTSafe returns when tsafe listener notifies a timestamp which meet the guarantee ts.
func (sd *shardDelegator) waitTSafe(ctx context.Context, ts uint64) (uint64, error) {
// already safe to search
latestTSafe := sd.latestTsafe.Load()
if latestTSafe >= ts {
return latestTSafe, nil
}
// check lag duration too large
st, _ := tsoutil.ParseTS(latestTSafe)
gt, _ := tsoutil.ParseTS(ts)
lag := gt.Sub(st)
maxLag := paramtable.Get().QueryNodeCfg.MaxTimestampLag.GetAsDuration(time.Second)
if lag > maxLag {
log.Warn("guarantee and serviceable ts larger than MaxLag",
zap.Time("guaranteeTime", gt),
zap.Time("serviceableTime", st),
zap.Duration("lag", lag),
zap.Duration("maxTsLag", maxLag),
)
return 0, WrapErrTsLagTooLarge(lag, maxLag)
}
ch := make(chan struct{})
go func() {
sd.tsCond.L.Lock()
defer sd.tsCond.L.Unlock()
for sd.latestTsafe.Load() < ts &&
ctx.Err() == nil &&
sd.Serviceable() {
sd.tsCond.Wait()
}
close(ch)
}()
for {
select {
// timeout
case <-ctx.Done():
// notify wait goroutine to quit
sd.tsCond.Broadcast()
return 0, ctx.Err()
case <-ch:
if !sd.Serviceable() {
return 0, merr.WrapErrChannelNotAvailable(sd.vchannelName, "delegator closed during wait tsafe")
}
return sd.latestTsafe.Load(), nil
}
}
}
pipeline先处理insert再delete会不会有问题
假设 客户端顺序发起了 insert A -> delete A -> insert A三个请求,结果被缓存到一起,同时被pipeline处理。当前pipeline是先处理insert、再处理delete的逻辑,最后按照 insert A -> insert A -> delete A的顺序处理。
由于segcore会把timestamp也保存起来,所以delete 的时候会根据timestamp进行可见性判断,不会删错数据。而且在强一致等级下,也不会看到中间状态——同时有两个“A”。
std::vector<SegOffset>
search_pk(const PkType& pk, Timestamp timestamp) const {
std::shared_lock lck(shared_mutex_);
std::vector<SegOffset> res_offsets;
auto offset_iter = pk2offset_->find(pk);
for (auto offset : offset_iter) {
if (timestamps_[offset] <= timestamp) {
res_offsets.emplace_back(offset);
}
}
return res_offsets;
}
总结
Milvus利用tso Timestamp和TimeTick,提供了四种一致性等级,并实现了类似MVCC的机制。
DDL
前面讲了DM和DQ任务的一致性。还有一种情况:DDL与DML的一致性。DDL任务没有走消息队列,由root coord直接处理,DML走消息队列,被worker处理,两条完全不同的路径。
DDL任务和DML任务一样,在proxy中入队时,会向 root coord 申请一个时间戳,所以DDL和DML是有序的,且可互相比较,一样走TimeTick的逻辑。
proxy为了避免频繁访问root coord,在本地缓存了collection 等元数据,同时提供了InvalidateCollectionMetaCache等接口,供root coord调用,来刷新本地缓存。同样。sdk也缓存了collection元数据,它的元数据刷新则依赖时间戳。元数据和普通数据一样也提供了MVCC的机制,读写时会指定timestamp。 暂时无法在飞书文档外展示此内容
func (c *Client) retryIfSchemaError(ctx context.Context, collName string, work func(ctx context.Context) (uint64, error)) error {
var lastTs uint64 = math.MaxUint64
return retry.Handle(ctx, func() (bool, error) {
ts, err := work(ctx)
if err != nil {
// if schema error
if errors.Is(err, merr.ErrCollectionSchemaMismatch) {
sameTs := ts == lastTs
lastTs = ts
if !sameTs {
c.collCache.Evict(collName)
}
// retry if not same ts
return !sameTs, err
}
return false, err
}
return false, nil
})
}
所以,主要靠MVCC + sdk内重试保证一致性。
参考
- https://tikv.org/deep-dive/distributed-transaction/timestamp-oracle/